

古脊椎动物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (2): 117-133.DOI: 10.19615/j.cnki.2096-9899.220402
收稿日期:2021-12-14
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-05-07
通讯作者:
wangshiqi@ivpp.ac.cn基金资助:
WANG Shi-Qi1,2( ), LI Chun-Xiao1,2,3
), LI Chun-Xiao1,2,3
Received:2021-12-14
Published:2022-04-20
Online:2022-05-07
Contact:
wangshiqi@ivpp.ac.cn摘要:
铲齿象(Platybelodon)在中国北方中中新世的长鼻类中占据着主导地位。然而,对其头骨和颊齿形态学的研究并不充分,尤其是与嵌齿象属(Gomphotherium)的区别并没有仔细研究。重新研究了之前被鉴定为陕西嵌齿象(Gomphotherium shensiense)的一件较为完整的头骨。这件标本上牙无釉质带,吻部窄长,面部位置靠前且伸长,有一个很大的“鼻前斜坡”。这些形态特征不同于已知任何嵌齿象的头骨,但与铲齿象的原始类群,如同心铲齿象(P. tongxinensis)和达氏铲齿象(P. danovi)相吻合;臼齿也和同心铲齿象正型标本M3一样,具有四脊,齿脊间距离较宽,外轮廓弯曲,有白垩质型齿发育的倾向。据以上特征,将陕西嵌齿象归为同心铲齿象,两者为同物异名。另外,还从美国自然历史博物馆中亚考察队在中国通古尔地区采集的一批格氏铲齿象(P. grangeri)材料中鉴定出一个新种四脊铲齿象(Platybelodon tetralophus sp. nov.)。不同于格氏铲齿象和其他的种,四脊铲齿象的M2和m2有4个齿脊,是铲齿象中最进步的种;它只在通古尔组的最上部层位出现,即属于铁木钦(Tamuqin)动物群的Platybelodon Quarry地点和Wolf Camp Quarry地点。本研究工作是对中国铲齿象属的全面修订。
中图分类号:
王世骐, 李春晓. 陕西嵌齿象与同心铲齿象同物异名考及铲齿象属一新种. 古脊椎动物学报, 2022, 60(2): 117-133.
WANG Shi-Qi, LI Chun-Xiao. Attributing “Gomphotherium shensiense” to Platybelodon tongxinensis, and a new species of Platybelodon from the latest Middle Miocene. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2022, 60(2): 117-133.
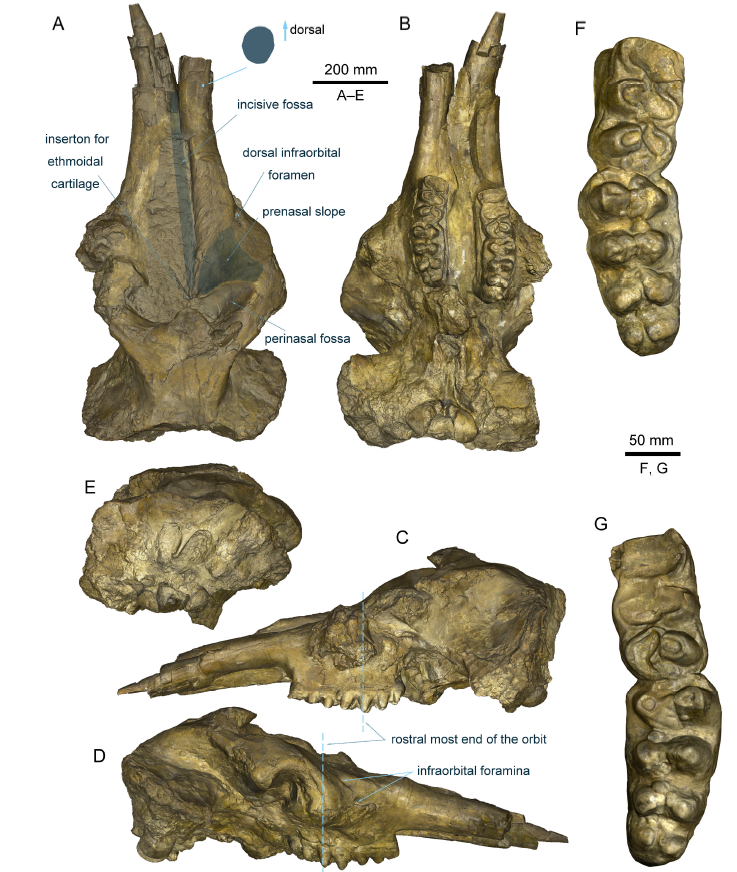
Fig. 1 Platybelodon tongxinensis, IVPP V 3084, cranium, from Tianhegou, Lintong, Shaanxi, the Lengshuigou Formation, in the dorsal (A), ventral (B), left lateral (C), right lateral (D), and caudal (E) views, as well as the right (F), and left (G) M2-M3 tooth rows, in the occlusal view
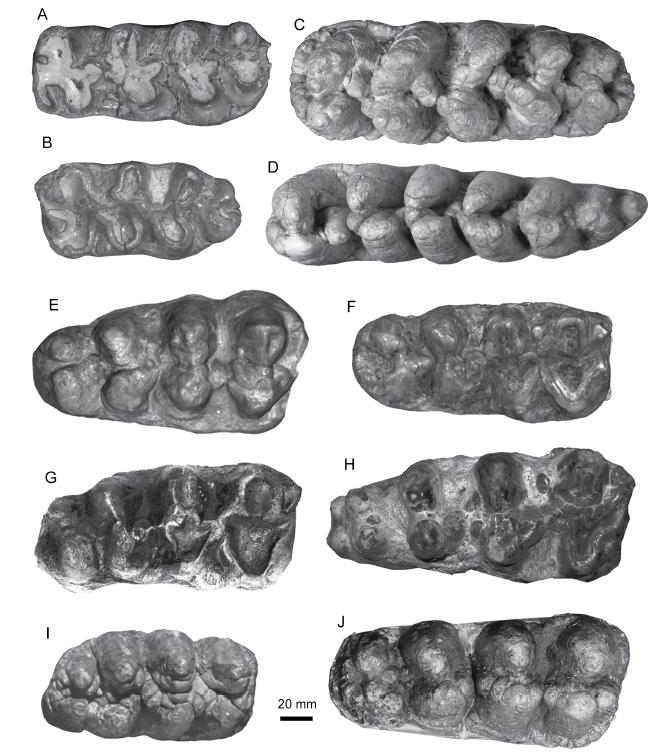
Fig. 2 Cheek teeth of Platybelodon and Gomphotherium in occlusal view A-D. Platybelodon tetralophus sp. nov., from the Platybelodon Quarry, Tamqin Fauna of the Tunggur region: A. AMHN 26574, left m2, the holotype; B. AMHN 26479, left M2; C. AMHN 26473, mirrored right M3;D. AMHN 26475, left m3; E. P. tongxinensis, IVPP V 3084, right M3 (holotype of Gomphotherium shensiense), from Tianhegou, Lintong; F. P. tongxinensis, IVPP V 5572, right M3, the holotype, from Shataigou, Tongxin; G. P. danovi, right M3, the holotype, from Kuban region, Caucasus, after Borissiak, 1929; H. P. grangeri, HMV 1788, right M3, from Hujialiang, Linxia;I. Gomphotherium angustiden, MNHN.F.SEP 266, right M3, from En Péjouan, after Tassy, 2014;J. G. connexum, IVPP V 8572, right M3, from the Halamagai Fauna, Ulungur region
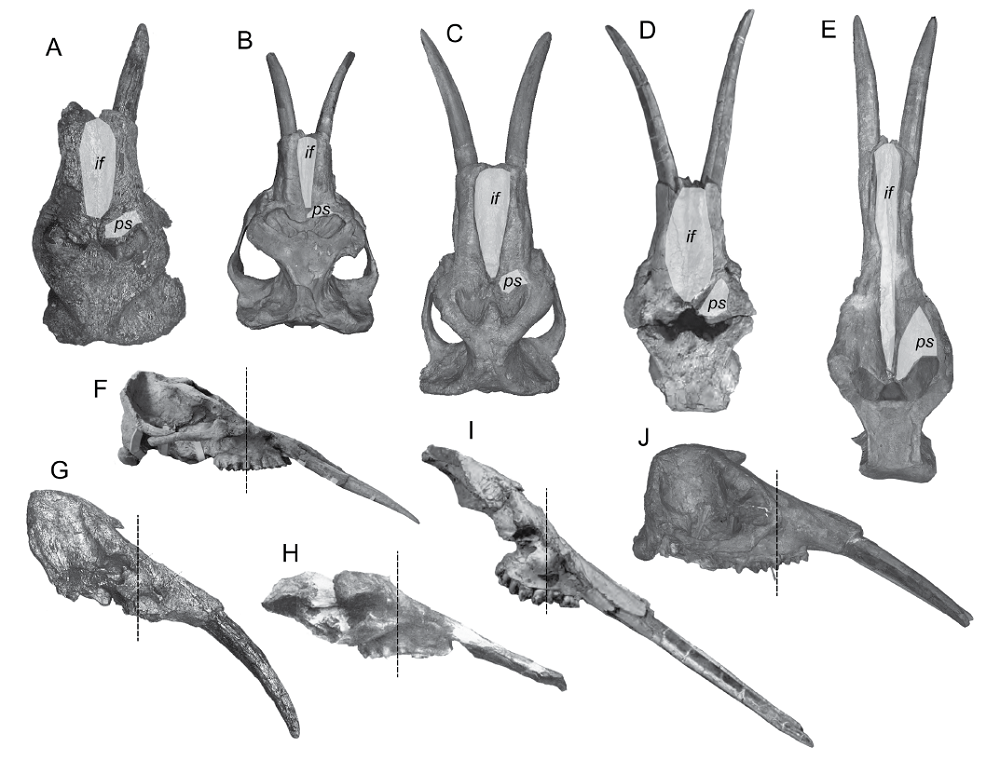
Fig. 3 Various crania of trilophodont gomphotheres, not to scale A-E. dorsal view, the white transparent areas indicating the incisive fossa (if) and prenasal slope (ps);F-J. lateral view, the vertical dash lines indicating the rostral end of the orbit A, G. Archaeobelodon aff. A. filholi, KNM MI 7532, from Mwiti, Kenya, after Tassy, 1986; B. Gomphotherium productum, AMNH 10582, from Clarendon, Texas; C, J. G. tassyi, IVPP V 22780, from Erdaoqu, Zhongning, Ningxia (upper Zhangenbao Formation); D, I. G. angustidens, MNHN.F.SEP 186, from En Péjouan, after (Tassy, 2013); E, F. Platybelodon grangeri, HMV 0939 (E) and 0940 (F), from Hujialiang, Linxia; H. P. danovi, the holotype, from Kuban region, Caucasus, after Borissiak, 1929
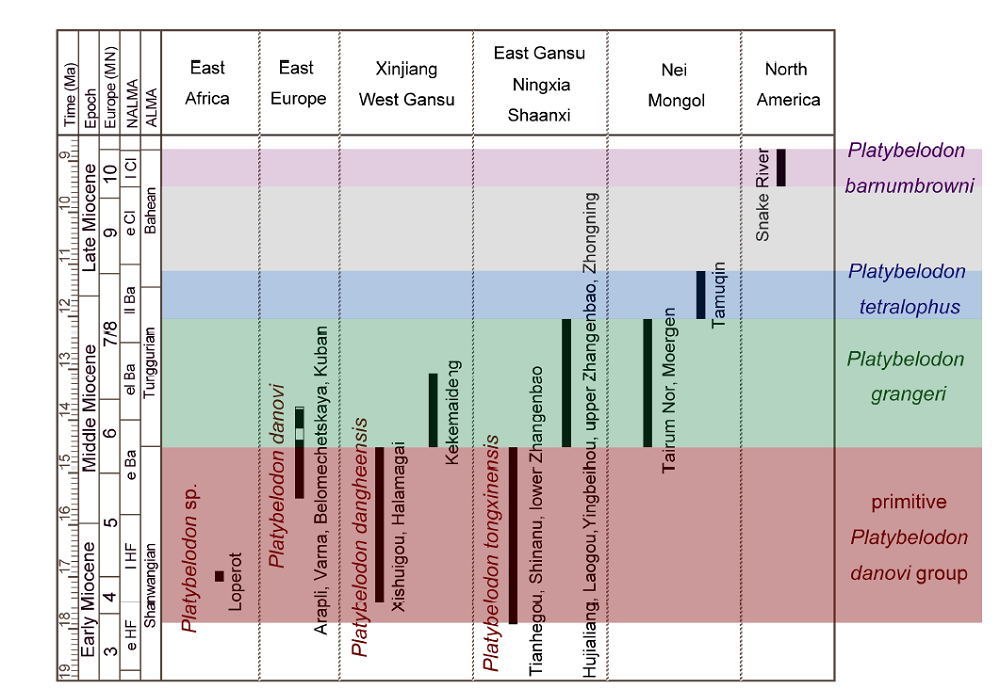
Fig. 5 Geograpical and biochronologic distribution of Platybelodon species Abbreviations: e Ba, early Barstovian; e Cl, early Clarendonian; e HF, early Hemingfordian; el Ba, early late Barstovian; l Cl, late Clarendonian; l HF, late Hemingfordian; ll Ba, late late Barstovian
| [1] | Barbour E H, 1927. Preliminary notice of a new proboscidean Amebelodon fricki, gen. et sp. nov. Bull Nebr State Mus, 1(13): 131-134 |
| [2] | Barbour E H, 1931. A new amebelodont, Torynobelodon barnumbrowni, sp. nov., a preliminary report. Bull Nebr State Mus, 1(22): 191-198 |
| [3] | Belyaeva E I, Gabunia L K, 1960. New finds concerning Platybelodontinae from the Casucasus. Tr Inst Paleobiol Akad Nuak Gruz SSR, 5: 63-105 |
| [4] | Borissiak A A, 1928. On a new mastodon from the Chokrak Beds (Middle Miocene) of the Kuban region, Platybelodon danovi, n. gen. n. sp. Ann Soc Paleont Russ, 7: 105-120 |
| [5] | Borissiak A A, 1929. On a new direction in the adaptive radiation of mastodonts. Palaeobiologica, 2: 19-33 |
| [6] | Chang H, Zhai R J, 1978. Miocene mastodonts of Lantian and Lintung, Shensi. Prof Pap Stratigr Palaeontol, 7: 136-142 |
| [7] | Chen G F, 1978. Mastodont remains form the Miocene of Zhongning-Tongxin region in Ningxia. Vert PalAsiat, 16(2): 103-110 |
| [8] | Cope E D, 1884. The extinct Mammalia of the valley of Mexico. Proc Am Philosoph Soc, 22: 1-21 |
| [9] | Falconer H, 1857. On the species of mastodon and elephant occurring in the fossil state in Great Britain. Part I. Mastodon. Quart J Geol Soc London, 13: 307-360 |
| [10] | Gabunia L K, 1973. The Belomechetskaya Fauna of Fossil Vertebrates. Tbilisi: Metsniyereba. 1-133 |
| [11] | Gaziry A W, 1976. Jungtertiäre Mastodonten aus Anatolien (Türkei). Geol Jahrb, B22: 3-143 |
| [12] | Gentry A W R, Rössener G E, Heizmann E P J, 1999. Suborder Ruminantia. In: Rössener G E, Heissig K eds. The Miocene Land Mammals of Europe. München: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. 225-258 |
| [13] |
Gheerbrant E, Tassy P, 2009. L'origine et l'évolution des éléphants. CR Palevol, 8: 281-294
DOI URL |
| [14] | Göhlich U B, 1999. Order Proboscidea. In: Rössener G E, Heissig K eds. The Miocene Land Mammals of Europe. München: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. 157-168 |
| [15] |
Göhlich U B, 2010. The Proboscidea (Mammalia) from the Miocene of Sandelzhausen (southern Germany). Paläontol Z, 84(1): 163-204
DOI URL |
| [16] | Guan J, 1991. The character analysis and phylogeny discussion on the shovel tusk mastodonts. Mem Beijing Nat Hist Mus, 50: 1-21 |
| [17] | Hilgen F J, Lourens L J, Dam J A van, 2012. Chapter 29, the Neogene period. In: Gradstein F M, Ogg J G, Schmitz M D et al. eds. The Geologic Time Scale 2012. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 923-978 |
| [18] | Illiger C D, 1811. Prodromus Systematis Mammalium et Avium Additis Terminis Zoographicis Uttriusque Classis. Berlin: Salfeld. 1-301 |
| [19] |
Konidaris G E, Roussiakis S J, 2018. The first record of Anancus (Mammalia, Proboscidea) in the late Miocene of Greece and reappraisal of the primitive anancines from Europe. J Vert Paleont, 38: e1534118
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Lambert W D, 1990. Rediagnosis of the genus Amebelodon (Mammalia, Proboscidea, Gomphotheriidae), with a new subgenus and species, Amebelodon (Konobelodon) britti. J Paleontol, 64(6): 1032-1040
DOI URL |
| [21] | Lambert W D, Shoshani J, 1998. Proboscidea. In: Janis C M, Scott K M, Jacobs L L eds. Evolution of Tertiary Mammals of North America. Vol 1: Terrestrial Carnivores, Ungulates, and Ungulatelike Mammals. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 606-621 |
| [22] |
Li Y K, Li Q, Ni X J, et al. 2020. The oldest known bovid from China and reappraisal of the Chinese “Eotragus”. Pap Palaeontol, 7: 913-929
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Li Y K, Mennecart B, Aiglstorfer M, et al. 2021. The early evolution of cranial appendages in Bovoidea revealed by new species of Amphimoschus (Mammalia: Ruminantia) from China. Zool J Linn Soc. Doi: 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlab053
DOI |
| [24] | Markov G N, 2008. Fossil proboscideans (Mammalia) from the vicinities of Varna: a rare indication of middle Miocene vertebrate fauna in Bulgaria. Hist Nat Bulg, 19: 137-152 |
| [25] | Osborn H F, 1929. The revival of Central Asiatic life. Nat Hist, 29: 2-16 |
| [26] | Osborn H F, Granger W, 1931. The shovel-tuskers, Amebelodontinae, of Central Asia. Am Mus Novit, 470: 1-12 |
| [27] | Osborn H F, Granger W, 1932. Platybelodon grangeri, three growth stages, and a new Serridentine from Mongolia. Am Mus Novit, 537: 1-13 |
| [28] |
Pickford M, Gabunia L, Mein P, et al. 2000. The middle Miocene mammalian site of Belometchetskaya, North Caucasus: an important biostratigraphic link between Europe and China. Geobios, 33: 257-267
DOI URL |
| [29] | Qiu Z D, Wang X M, Li Q, 2013. Neogene faunal succession and biochronology of Central Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia). In: Wang X M, Flynn L J, Fortelius M eds. Neogene Terrestrial Mammalian Biostratigraphy and Chronology of Asia. New York: Columbia University Press. 155-186 |
| [30] | Qiu Z X, Qiu Z D, 1990. Chronological sequence and subdivision of Chinese Neogene local mammalian faunas. J Stratigr, 14(4): 241-260 |
| [31] | Sanders W J, Gheerbrant E, Harris J M, et al. 2010. Proboscidea. In: Werdelin L, Sanders W J eds.eds. Cenozoic Mammals of Africa. Berkeley: University of California Press. 161-251 |
| [32] | Schlesinger G, 1917. Die Mastodonten des K. K. Naturhistorischen Hofmuseums. Denkschr K K Naturhist Hofm Geol-paläont, 1: 1-231 |
| [33] |
Sun J, Ye J, Wu W Y, et al. 2010. Late Oligocene-Miocene mid-latitude aridification and wind patterns in the Asian interior. Geology, 38: 515-518
DOI URL |
| [34] | Tassy P, 1986. Nouveaux Elephantoidea (Proboscidea, Mammalia) dans le Miocène du Kenya: essai de réévaluation systématique. Ph. D thesis. Paris: Cahiers de Paléontologie. Éditions du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, (CNRS). 1-135 |
| [35] |
Tassy P, 1994. Gaps, parsimony, and early Miocene elephantoids (Mammalia), with a re-evaluation of Gomphotherium annectens (Matsumoto, 1925). Zool J Linn Soc, 112: 101-117
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Tassy P, 2013. L'anatomie cranio-mandibulaire de Gomphotherium angustidens (Cuvier, 1817) (Proboscidea, Mammalia): Données issues du gisement d'En Péjouan (Miocène moyen du Gers, France). Geodiversitas, 35(2): 377-445
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Tassy P, 2014. L'odontologie de Gomphotherium angustidens (Cuvier, 1817) (Proboscidea, Mammalia): Données issues du gisement d'En Péjouan (Miocène moyen du Gers, France). Geodiversitas, 36(1): 35-115
DOI URL |
| [38] | Tobien H, Chen G, Li Y, 1986. Mastodonts (Proboscidea, Mammalia) from the Late Neogene and Early Pleistocene of the People’s Republic of China, part I: historical account: the genera Gomphotherium, Choerolophodon, Synconolophus, Amebelodon, Platybelodon, Sinomastodon. Mainzer Geowiss Mitt, 15: 119-181 |
| [39] | Wang B Y, Qiu Z X, 2002. A new species of Platybelodon (Gomphotheriidae, Proboscidea, Mammalia) from early Miocene of the Danghe area, Gansu, China. Vert PalAsiat, 40(4): 291-299 |
| [40] | Wang J, 2021. Vegetation History in Northern China and its Response to Critical Geological and Environmental Events Since the Neogene. Ph. D thesis. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. 1-193 |
| [41] | Wang S Q, He W, Chen S Q, 2013. Gomphotheriid mammal Platybelodon from the Middle Miocene of Linxia Basin, Gansu, China. Acta Palaeontol Pol, 58(2): 221-240 |
| [42] |
Wang S Q, Deng T, Tang T, et al. 2015a. Evolution of Protanancus (Proboscidea, Mammalia) in East Asia. J Vert Paleont, 35(1): 1-13
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Wang S Q, Duangkrayom J, Yang X W, 2015b. Occurrence of the Gomphotherium angustidens group in China, based on a revision of Gomphotherium connexum (Hopwood, 1935) and Gomphotherium shensiensis Chang and Zhai, 1978: continental correlation of Gomphotherium species across the Palearctic. Paläontol Z, 89: 1073-1086
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Wang S Q, Deng T, Ye J, et al. 2017. Morphological and ecological diversity of Amebelodontidae (Proboscidea, Mammalia) revealed by a Miocene fossil accumulation of an upper-tuskless proboscidean. J Syst Palaeontol, 15(8): 601-615
DOI URL |
| [45] | Ye J, Jia H, 1986. Platybelodon (Proboscidea, Mammalia) from the middle Miocene of Tongxin, Ningxia. Vert PalAsiat, 24(2): 139-151 |
| [46] | Ye J, Qiu Z X, Chen J Z, 1989. Comparative study of a juvenile skull of Platybelodon tongxinensis. Vert PalAsiat, 27(4): 284-330 |
| [47] | Ye J, Wu W Y, Ni X J, et al. 2012. The Duolebulejin Section of northern Junggar Basin and its stratigraphic and environmental implication. Sci China Earth Sci, 42(10): 1523-1532 |
| [1] | 山显任, 林翔鸿, 张雨萌, 李旭彤, 盖志琨. 西域鱼在江西和塔里木盆地志留系的新发现. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(4): 245-260. |
| [2] | 刘金毅, 张颖奇, 迟振卿, 王永, 杨劲松, 郑绍华. 泥河湾盆地叶沟晚上新世贺风三趾马动物群及其生物地层学意义. 古脊椎动物学报, 2022, 60(4): 278-323. |
| [3] | Joonas Wasiljeff, 张兆群. 内蒙古阿拉善左旗乌兰塔塔尔最晚始新世-渐新世剖面的区域年代地层意义. 古脊椎动物学报, 2022, 60(1): 42-53. |
| [4] | 张立民, 董为, 倪喜军, 李强. 晚中新世晚期土城子小哺乳动物组合及土城子动物群在内蒙古中部地区新近纪哺乳动物群序列中的位置. 古脊椎动物学报, 2021, 59(1): 45-63. |
| [5] | 董为, 刘文晖, 白炜鹏. 中国境内部分更新世哺乳动物群的支序系统学分析及生物年代学推断. 古脊椎动物学报, 2020, 58(1): 67-81. |
| [6] | 杨湘雯,李 雨, 王世骐 . 临夏盆地中中新统维曼嵌齿象(Gomphotherium wimani) (长鼻目,嵌齿象科)的头骨及颊齿. 古脊椎动物学报, 2017, 55(4): 331-346. |
| [7] | Philip D. GINGERICH . 美国怀俄明州大角盆地北部Polecat台地古新世动物群演化. 古脊椎动物学报, 2016, 54(3): 212-234. |
| [8] | 王世骐,刘善品,颉光普,刘 佳,彭廷江,侯素宽. 甘肃天水武山县南峪村的维曼嵌齿象及其生物地层学意义. 古脊椎动物学报, 2013, 51(1): 71-84. |
| [9] | 王晓鸣, 颉光普, 李强, 邱铸鼎, 曾志杰, Gary T. TAKEUCHI, 王伴月, 傅铭楷, Asta ROSENSTRÖM-FORTELIUS, Håkan WAHLQUIST, 董维霖, 张春福, 王杨. 步林在青海柴达木盆地的早期工作记录——经典脊椎动物化石地点与现代地层框架的解译. 古脊椎动物学报, 2011, 49(3): 285-310. |
| [10] | 刘丽萍,郑绍华,张兆群,王李花. 甘肃董湾晚新近纪地层及中新统/上新统界线. 古脊椎动物学报, 2011, 49(2): 229-240. |
| [11] | Pieter Missiaen. 亚洲早古近纪哺乳动物生物年代学与生物地理学的新认识. 古脊椎动物学报, 2011, 49(1): 29-52. |
| [12] | 王元青,孟津,金迅,毕丛山,白滨,李萍,倪喜军,李茜,Daniel L. GEBO. 内蒙古二连盆地早始新世脑木根组上部的奇蹄类. 古脊椎动物学报, 2011, 49(1): 123-140. |
| [13] | 王晓鸣,邱铸鼎,李强,富田幸光,木村由莉,曾志杰,王洪江. 内蒙古中部敖尔班地区的岩石及生物地层. 古脊椎动物学报, 2009, 47(2): 111-134. |
| [14] | 李 强 , 郑绍华 , 蔡保全. 泥河湾盆地上新世生物地层序列与环境. 古脊椎动物学报, 2008, 46(3): 210-232. |
| [15] | 孟 津, 叶 捷, 吴文裕, 倪喜军 , 毕顺东. 新疆准噶尔盆地北缘新近系顶山盐池组及相关地层问题. 古脊椎动物学报, 2008, 46(2): 90-110. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||