

古脊椎动物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 63 ›› Issue (1): 57-80.DOI: 10.19615/j.cnki.2096-9899.241120CSTR: 32090.14.j.cnki.2096-9899.241120
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-04-19
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-26
通讯作者:
* dengtao@ivpp.ac.cn基金资助:
SUN Bo-Yang1, LIU Yan1, WANG Shi-Qi1, DENG Tao1,2,*(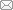 )
)
Received:2024-04-19
Published:2025-01-20
Online:2025-01-26
Contact:
* dengtao@ivpp.ac.cn摘要:
对一个具有争议的类群Hipparion plocodus进行了回顾。山西保德的头骨材料具有明确的鉴定特征,证实Hi. plocodus为一有效种。使用新的特征矩阵进行系统发育分析,表明Hi. plocodus和欧洲种Hippotherium malpassii构成一个单系群。事实上所谓的Hm. malpassii和Hippotherium属无较近的亲缘关系,而该属目前无晚中新世晚期分布记录。因此之前所定义的Hi. plocodus和Hm. malpassii在更好的材料发现之前暂时归入“Hipparion” 属当中。二者演化水平略有差异,时代相当,表明它们独立起源于某一更原始类群。在晚中新世晚期,亚洲夏季风的盛行加强了中国地区的湿润程度,森林和灌木林生境在这一背景下迅速扩张,最终令欧亚大陆某一喜好封闭环境的类群向中国扩散,在这片适应的土地上演化出了“Hi.” plocodus。
中图分类号:
孙博阳, 刘艳, 王世骐, 邓涛. 旧大陆“Hippotherium”的存续:两种欧亚大陆三趾马的修订. 古脊椎动物学报, 2025, 63(1): 57-80.
SUN Bo-Yang, LIU Yan, WANG Shi-Qi, DENG Tao. Occurrence of “Hippotherium” in the Old World: a revision of two hipparion species in Eurasia. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2025, 63(1): 57-80.
| item | M 3824 | M 3825 | AM 146439 | AM 146440 | AM 146441 | AM 146442 | AM 146443 | AM 146448 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| muzzle length | 117.2 | 107.9 | 114.1 | 109.5 | 108 | 109 | |||
| palatal length | 101.3 | 104.4 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 103.5 | 103.8 | 104.1 | 96 | |
| vomerine length | 92.2 | ||||||||
| premolar length | 74.7 | 75.7 | 67.6 | 73.1 | 67.9 | 73.8 | 71.4 | 63.8 | |
| molar length | 59.5 | 59 | 52.9 | 57.7 | 56.8 | 60.9 | 57.9 | 54.5 | |
| upper cheek teeth length | 136 | 137 | 120.3 | 128.7 | 125.5 | 134.9 | 130.3 | 118.3 | |
| minimal breadth of choanae | 33.7 | 34.1 | 30.3 | 31 | |||||
| maximal breadth of choanae | 36.3 | 41 | 39 | 35.5 | 37.2 | ||||
| palatal breadth | 66.6 | 64.9 | 58.3 | 59.3 | 59.4 | 63.2 | 57 | 53.1 | |
| minimal muzzle breadth | 35.5 | 35.3 | 35.5 | 35.9 | 37.1 | 35.7 | |||
| muzzle breadth | 42 | 46.9 | 52.5 | 55.4 | 51.6 | 48.6 | |||
| frontal breadth | 140.5 | ||||||||
| anterior ocular line | 311.8 | ||||||||
| facial height | 83.7 | ||||||||
| antero-posterior orbital diameter | 53.4 | ||||||||
| orbital diameter perpendicular to the former | 50.2 | ||||||||
| length of the naso-incisival notch | 113.3 | 109 | |||||||
| cheek length | 150.5 | 149.7 | 151.6 | ||||||
| POB length | 37.2 | 32.1 | 40.9 | 37 | 30.8 | ||||
| POF length | 90.3 | 81.5 | 87.2 | 87.3 | |||||
| distance between the back of POF and IOF | 60.6 | 57.9 | 60.6 | ||||||
| height of the POF | 42.4 | 43.5 | 43 | 52.3 | |||||
| distance between POF and the facial crest | 24.3 | 41.3 | 36.2 | 40 | 27.6 | ||||
| height of back of IOF | 47.9 | 43.1 | 45.6 | ||||||
| height of the back of POF above the alveolar border | 72.3 | 75.6 | 69.4 | 82.5 | 77.2 |
Table 1 Skull measurements of “Hipparion” plocodus (mm)
| item | M 3824 | M 3825 | AM 146439 | AM 146440 | AM 146441 | AM 146442 | AM 146443 | AM 146448 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| muzzle length | 117.2 | 107.9 | 114.1 | 109.5 | 108 | 109 | |||
| palatal length | 101.3 | 104.4 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 103.5 | 103.8 | 104.1 | 96 | |
| vomerine length | 92.2 | ||||||||
| premolar length | 74.7 | 75.7 | 67.6 | 73.1 | 67.9 | 73.8 | 71.4 | 63.8 | |
| molar length | 59.5 | 59 | 52.9 | 57.7 | 56.8 | 60.9 | 57.9 | 54.5 | |
| upper cheek teeth length | 136 | 137 | 120.3 | 128.7 | 125.5 | 134.9 | 130.3 | 118.3 | |
| minimal breadth of choanae | 33.7 | 34.1 | 30.3 | 31 | |||||
| maximal breadth of choanae | 36.3 | 41 | 39 | 35.5 | 37.2 | ||||
| palatal breadth | 66.6 | 64.9 | 58.3 | 59.3 | 59.4 | 63.2 | 57 | 53.1 | |
| minimal muzzle breadth | 35.5 | 35.3 | 35.5 | 35.9 | 37.1 | 35.7 | |||
| muzzle breadth | 42 | 46.9 | 52.5 | 55.4 | 51.6 | 48.6 | |||
| frontal breadth | 140.5 | ||||||||
| anterior ocular line | 311.8 | ||||||||
| facial height | 83.7 | ||||||||
| antero-posterior orbital diameter | 53.4 | ||||||||
| orbital diameter perpendicular to the former | 50.2 | ||||||||
| length of the naso-incisival notch | 113.3 | 109 | |||||||
| cheek length | 150.5 | 149.7 | 151.6 | ||||||
| POB length | 37.2 | 32.1 | 40.9 | 37 | 30.8 | ||||
| POF length | 90.3 | 81.5 | 87.2 | 87.3 | |||||
| distance between the back of POF and IOF | 60.6 | 57.9 | 60.6 | ||||||
| height of the POF | 42.4 | 43.5 | 43 | 52.3 | |||||
| distance between POF and the facial crest | 24.3 | 41.3 | 36.2 | 40 | 27.6 | ||||
| height of back of IOF | 47.9 | 43.1 | 45.6 | ||||||
| height of the back of POF above the alveolar border | 72.3 | 75.6 | 69.4 | 82.5 | 77.2 |
| Teeth | N | Measures | Avg | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | 4 | L | 27.4 | 24.9 | 28.6 |
| 2 | W | 20.8 | 19 | 22.5 | |
| 3 | PL | 6.7 | 5.6 | 8.4 | |
| 2 | PW | 3.7 | 3.4 | 4 | |
| P3 | 6 | L | 21.3 | 18.6 | 22.6 |
| 5 | W | 21.6 | 20.6 | 23 | |
| 6 | PL | 6.3 | 4.9 | 8 | |
| 5 | PW | 4.1 | 3.1 | 5.2 | |
| P4 | 6 | L | 20.0 | 18.7 | 21.3 |
| 5 | W | 21.0 | 20.2 | 22.4 | |
| 6 | PL | 6.0 | 4.8 | 7 | |
| 6 | PW | 4.4 | 3.3 | 5.7 | |
| M1 | 6 | L | 17.7 | 16.2 | 19.2 |
| 5 | W | 19.4 | 18.9 | 20.1 | |
| 6 | PL | 6.1 | 4.6 | 6.7 | |
| 6 | PW | 4.0 | 2.7 | 5.1 | |
| M2 | 6 | L | 18.0 | 16.4 | 19.1 |
| 4 | W | 19.0 | 18.3 | 19.8 | |
| 6 | PL | 5.7 | 4.7 | 6.4 | |
| 5 | PW | 4.1 | 3 | 4.8 | |
| M3 | 6 | L | 20.4 | 19.1 | 22.9 |
| 5 | W | 18.4 | 15.7 | 24 | |
| 6 | PL | 5.6 | 5.1 | 6 | |
| 5 | PW | 3.6 | 2.5 | 4.9 |
Table 2 Upper cheek tooth measurements of “Hipparion” plocodus (mm)
| Teeth | N | Measures | Avg | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | 4 | L | 27.4 | 24.9 | 28.6 |
| 2 | W | 20.8 | 19 | 22.5 | |
| 3 | PL | 6.7 | 5.6 | 8.4 | |
| 2 | PW | 3.7 | 3.4 | 4 | |
| P3 | 6 | L | 21.3 | 18.6 | 22.6 |
| 5 | W | 21.6 | 20.6 | 23 | |
| 6 | PL | 6.3 | 4.9 | 8 | |
| 5 | PW | 4.1 | 3.1 | 5.2 | |
| P4 | 6 | L | 20.0 | 18.7 | 21.3 |
| 5 | W | 21.0 | 20.2 | 22.4 | |
| 6 | PL | 6.0 | 4.8 | 7 | |
| 6 | PW | 4.4 | 3.3 | 5.7 | |
| M1 | 6 | L | 17.7 | 16.2 | 19.2 |
| 5 | W | 19.4 | 18.9 | 20.1 | |
| 6 | PL | 6.1 | 4.6 | 6.7 | |
| 6 | PW | 4.0 | 2.7 | 5.1 | |
| M2 | 6 | L | 18.0 | 16.4 | 19.1 |
| 4 | W | 19.0 | 18.3 | 19.8 | |
| 6 | PL | 5.7 | 4.7 | 6.4 | |
| 5 | PW | 4.1 | 3 | 4.8 | |
| M3 | 6 | L | 20.4 | 19.1 | 22.9 |
| 5 | W | 18.4 | 15.7 | 24 | |
| 6 | PL | 5.6 | 5.1 | 6 | |
| 5 | PW | 3.6 | 2.5 | 4.9 |
| Tooth | item | Measurement | Tooth | item | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2 | L | 26.6 | m1 | L | 19.8 |
| W | 12.7 | W | 11.7 | ||
| FL | 11.2 | FL | 8.1 | ||
| FI | 42.1 | FI | 40.9 | ||
| p3 | L | 22.9 | m2 | L | 20.3 |
| W | 14.7 | W | 10.8 | ||
| FL | 10.1 | FL | 7.2 | ||
| FI | 44.1 | FI | 35.5 | ||
| p4 | L | 21.2 | |||
| W | 14.4 | ||||
| FL | 8.9 | ||||
| FI | 42.0 |
Table 3 Lower cheek tooth measurements of AMNH F:AM 146708 (mm)
| Tooth | item | Measurement | Tooth | item | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p2 | L | 26.6 | m1 | L | 19.8 |
| W | 12.7 | W | 11.7 | ||
| FL | 11.2 | FL | 8.1 | ||
| FI | 42.1 | FI | 40.9 | ||
| p3 | L | 22.9 | m2 | L | 20.3 |
| W | 14.7 | W | 10.8 | ||
| FL | 10.1 | FL | 7.2 | ||
| FI | 44.1 | FI | 35.5 | ||
| p4 | L | 21.2 | |||
| W | 14.4 | ||||
| FL | 8.9 | ||||
| FI | 42.0 |
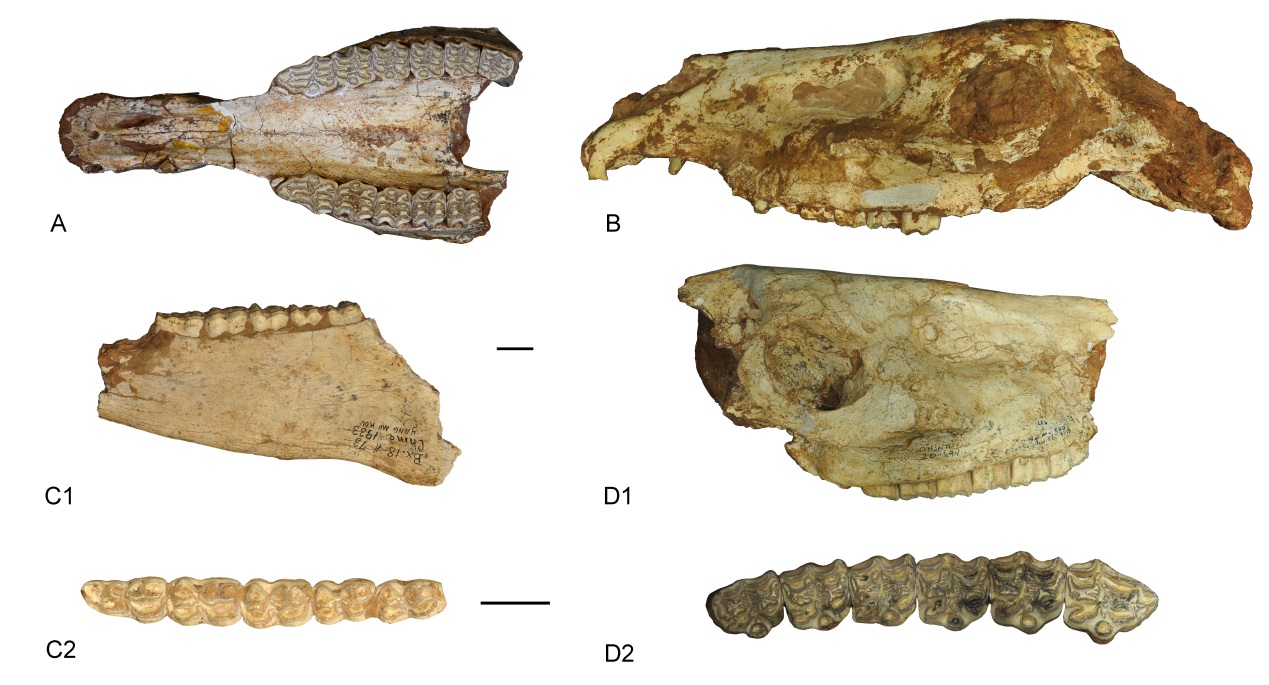
Fig. 1 “Hipparion” plocodus in Lok. 49, Baode, Shanxi A. ventral view of lectotype PMU M 3824; B. left view of AMNH F:AM 146448; C. AMNH F:AM 146708: C1. left view, C2. occlusal view of cheek tooth row; D. AMNH F:AM 146443: D1. left view, D2. occlusal view of left cheek tooth row. Scale bars = 2 cm
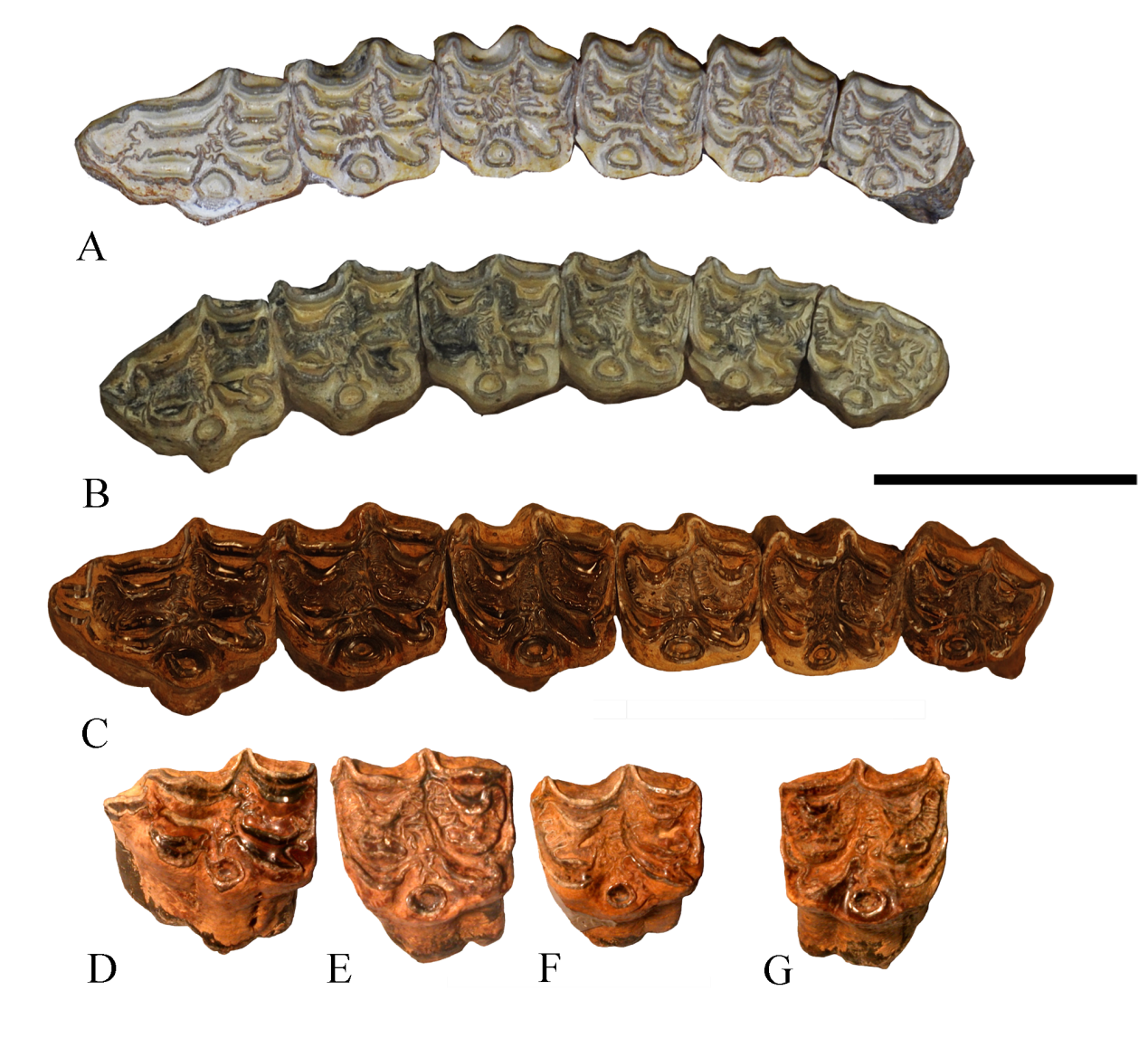

Fig. 2 Comparison on occlusal morphology of upper cheek teeth of “Hipparion” plocodus and “Hi.” malpassii A. left cheek tooth row of lectotype of “Hi.” plocodus, PMU M 3824; B. left cheek tooth row of “Hi.” plocodus, AMNH F:AM 146443; C. left cheek tooth row of holotype of “Hi.” malpassii, IGF 9400V (Bernor et al., 2011:fig. 13b); D. left P2 of “Hi.” malpassii, NHMB JH 126A (Bernor et al., 2011:fig. 15b); E. left P3 of “Hi.” malpassii, NHMB JH 126B (Bernor et al., 2011:fig. 15c); F. left M1 of “Hi.” malpassii, NHMB JH 126D (Bernor et al., 2011:fig. 15e);G. right P4 of “Hi.” malpassii, NHMB JH 126F (Bernor et al., 2011:fig. 15f). Scale bar = 4 cm
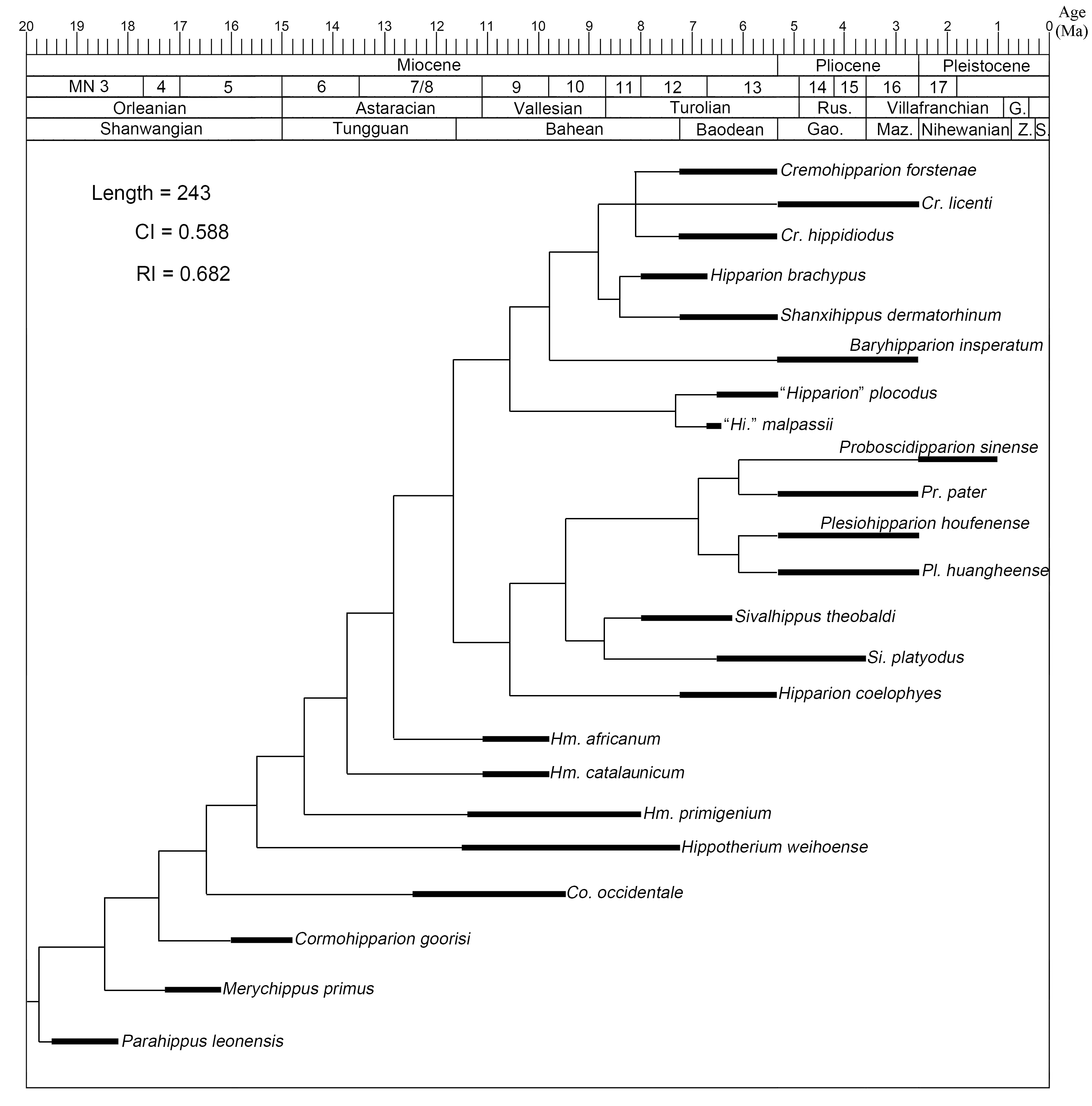
Fig. 3 Correlation of geographical distributions and phylogenetic relationship of Cormohipparion and Eurasian hipparion lineage based on the strict consensus tree from most-parsimonious trees Abbreviations: CI. consistency indece; G. Galerian; Gao. Gaozhuangian; Maz. Mazegouan; MN. European Neogene Mammal units; RI. consistency indece; Rus. Ruscinian; S. Salawusuan; Z. Zhoukoudianian
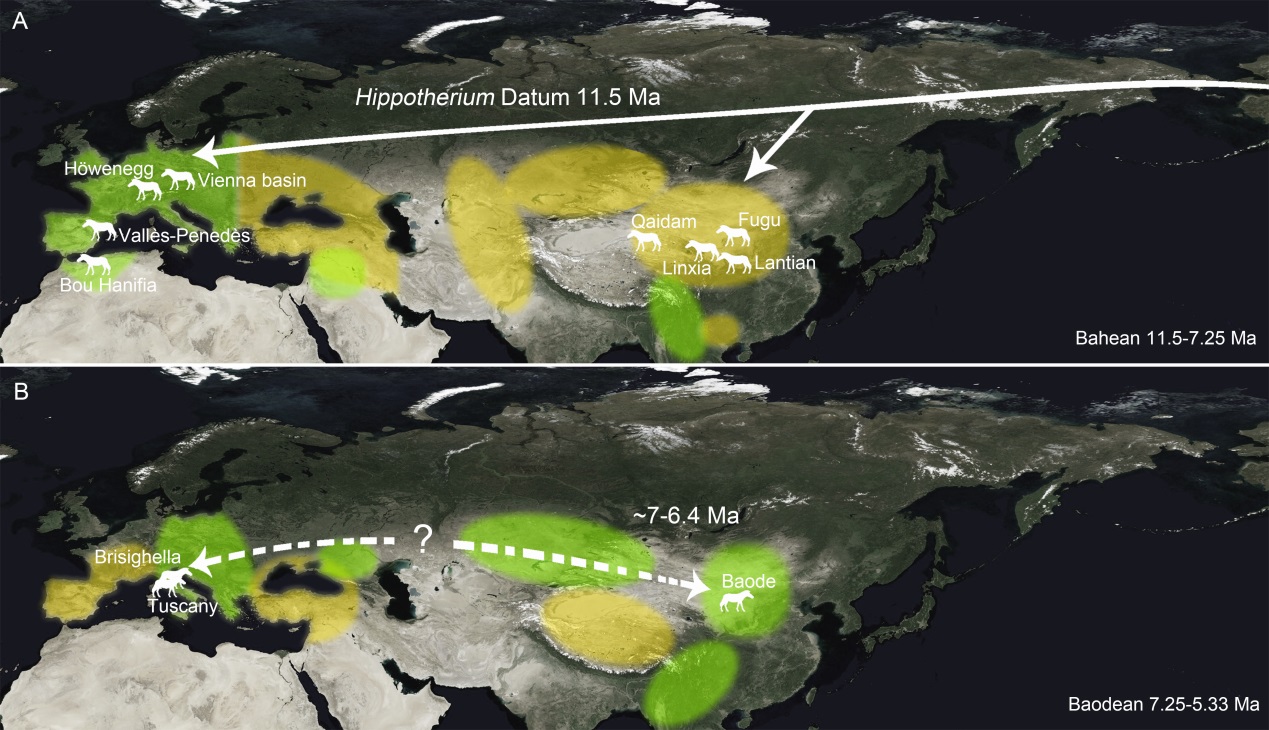
Fig. 4 Paleozoogeographical comparison of hipparion taxa in Bahean (A) and Baodean (B) Dispersal routes are referred to Garcés et al. (1997) and present research Greens and yellows distributed in Mid-latitude Asia, Europe and North Africa after Fortelius et al. (2014), respectively show the relatively close and open habitat
| [1] | Alberdi M T, 1989. A review of Old World hipparionine horses. In: Rrothero D R, Schoch R M eds. The Evolution of Perissodactyls. New York, Oxford: Oxford University Press. 234-261 |
| [2] | Bernor R L, 1985. Systematic and evolutionary relationships of the hipparionine horses from Maragheh, Iran (Late Miocene, Turolian age). Palaeovertebrata, 15(4): 173-269 |
| [3] | Bernor R L, Hussain S T, 1985. An assessment of the systematic, phylogenetic and biogeographic relationships of Siwalik hipparionine horses. J Vert Paleont, 5: 32-87 |
| [4] | Bernor R L, White T D, 2009. Systematics and biogeography of “Cormohipparion” africanum, early Vallesian (MN 9, ca. 10.5 Ma) of Bou Hanifia, Algeria. In: Albright B ed. Papers on Geology, Vertebrate Paleontology, and Biostratigraphy in Honor of Michael O. Woodburne. Bull Mus North Arizona, 65: 635-658 |
| [5] | Bernor R L, Qiu Z X, Tobien H, 1987. Phylogenetic and biogeographic bases for an Old World hipparionine horse geochronology. Proceedings of the VIIIth International Congress of the Regional Committee on Mediterranean Neogene Stratigraphy, Budapest. Ann Inst Geol Publ Hung, 70: 43-53 |
| [6] | Bernor R L, Qiu Z X, Hayek L A C, 1990. Systematic revision of Chinese hipparion species desribed by Sefve, 1927. Am Mus Novit, 2984: 1-60 |
| [7] | Bernor R L, Koufos G D, Woodburne M O et al., 1996. The evolutionary history and biochronology of European and southwestern Asian late Miocene and Pliocene hipparionine horses. In: Bernor R L, Fahlbusch V, Mittmann H W eds. The Evolution of Western Eurasian Neogene Mammal Faunas. New York: Columbia University Press. 307-338 |
| [8] | Bernor R L, Tobien H, Hayek L A C et al., 1997. Hippotherium primigenium (Equidae, Mammalia) from the late Miocene of Höwenegg (Hegau, Germany). Andrias, 10: 1-230 |
| [9] | Bernor R L, Kaiser T M, Kordos L et al., 1999. Stratigraphic context, systematic position and paleoecology of Hippotherium sumegense Kretzoi, 1984 from MN 10 (late Vallesian of the Pannonian Basin). Mitt Bayer Staatsslg Paläont Hist Geol, 39: 115-149 |
| [10] | Bernor R L, Armour-Chelu M, Kaiser T M et al., 2003. An evaluation of the late MN9 (Late Miocene, Vallesian age), Hipparion assemblage from Rudabánya (Hungary): systematic background, functional anatomy and palaeoecology. Coloq Palaeontol, Ext, 1: 35-45 |
| [11] | Bernor R L, Kaiser T M, Nelson S V et al., 2011. Systematics and paleobiology of Hippotherium malpassii n. sp. (Equidae, Mammalia) from the latest Miocene of Baccinello V3 (Tuscany, Italy). Boll Soc Paleontol Ital, 50(3): 175-208 |
| [12] | Bernor R L, Göhlich U B, Harzhauser M et al., 2017. The Pannonian C hipparions from the Vienna Basin. Palaegeogr Palaeoclim Palaeoecol, 476: 28-41 |
| [13] | Bernor R L, Wang S Q, Liu Y et al., 2018. Shanxihippus dermatorhinus (new gen.) with comparisons to Old World hipparions with specialized nasal apparati. Riv Ital Paleontol Stratigr, 124: 361-386 |
| [14] | Bernor R L, Cirilli O, Mittmann H W, 2022. Höwenegg Hippotherium primigenium: geological context, cranial and postcranial morphology, palaeoecological and biogeographic importance. Hist Biol, 35(8): 1376-1390 |
| [15] | Deng T, 2012. A skull of Hipparion (Proboscidipparion) sinense (Perissodactyla, Equidae) from Longdan, Dongxiang of northwestern China - addition to the Early Pleistocene Longdan mammalian fauna (3). Vert PalAsiat, 50: 74-84 |
| [16] | Deng T, Wang W M, Yue L P et al., 2004. New advances in the establishment of the Neogene Baode Stage. J Stratigr, 28(1): 41-47 |
| [17] | Deng T, Qiu Z X, Wang B Y et al., 2013. Chapter 9: Late Cenozoic Biostratigraphy of the Linxia Basin, Northwestern China. In: Wang X M, Flynn L J, Fortelius M eds. Fossil Mammals of Asia: Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology. New York: Columbia University Press. 243-273 |
| [18] | Deng T, Wang H J, Wang X M et al., 2016. The Late Miocene Hipparion (Equidae, Perissodactyla) fossils from Baogeda Ula, Inner Mongolia, China. Hist Biol, 28: 53-68 |
| [19] | Eisenmann V, Alberdi M T, de Giuli C et al., 1988. Methodology. In: Woodburne M, Sondaar P eds. Studying Fossil Horses. Leiden: E J Brill. 1-71 |
| [20] | Fang X, Wang J, Zhang W et al., 2016. Tectonosedimentary evolution model of an intracontinental flexural (foreland) basin for paleoclimatic research. Glob Planet Change, 145: 78-97 |
| [21] | Forstén A M, 1968. Revision of the Palearctic Hipparion. Acta Zool Fenn, 119: 1-134 |
| [22] | Forstén A M, 1985. Chinese Turolian Hipparion in the Lagrelius Collection. In: Lucas S G, Mateer N J eds. Studies in Chinese Fossil Vertebrates. Bull Geol Inst Univ Upps, New Ser, 11: 113-124 |
| [23] | Fortelius M, Eronen J T, Kaya F et al., 2014. Evolution of Neogene mammals in Eurasia: environmental forcing and biotic interactions. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci, 42: 579-604 |
| [24] | Garcés M, Cabrera L, Agustí J et al., 1997. Old World first appearance Datum of “Hipparion” horses: Late Miocene large-mammal dispersal and global events. Geology, 25(1): 19-22 |
| [25] | Goloboff P A, Farris J S, Nixon K C, 2008. TNT, a free program for phylogenetic analysis. Cladistics, 24: 774-786 |
| [26] | Gromova V, 1952. Le genre Hipparion. Bur Rech Geol Min, 12: 1-288 |
| [27] | Kaakinen A, Passey B H, Zhang Z Q et al., 2013. Chapter 7: Stratigraphy and paleoecology of the classical dragon bone localities of Baode County, Shanxi Province. In: Wang X M, Flynn L J, Fortelius M eds. Fossil Mammals of Asia: Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology. New York: Columbia University Press. 203-217 |
| [28] | Kaiser T M, Bernor R L, Scott R S et al., 2003. New interpretations of the systematics and palaeoecology of the Dorn-Dürkheim 1 hipparions (Late Miocene, Turolian Age [MN11]), Rheinhessen, Germany. Senckenbergiana lethaea, 83: 103-133 |
| [29] | Li Y F, Sun B Y, Deng T et al., 2023. Late Miocene Hipparion (Equidae, Perissodactyla) fossils from Fugu, northern Shaanxi, China, and their stratigraphic significance. J Mamm Evol, 30: 657-671 |
| [30] | Liu Y, 2013. Late Miocene hipparionine fossils from Lantian, Shaanxi Province and phylogenetic analysis on Chinese Hipparionines. Ph. D thesis. Beijng: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. 1-130 |
| [31] | MacFadden B J, Woodburne M O, 1982. Systematics of the Neogene Siwalik hipparions (Mammalia, Equidae) based on cranial and dental morphology. J Vert Paleont, 2: 185-218 |
| [32] | Pang L B, 2015. Hipparion (Equidae, Perissodactyla) fossils from the Shilei Locality of the Linxia Basin, Gansu Provinve. Quat Sci, 35(3): 502-512 |
| [33] | Qiu Z X, Huang W L, Guo Z H, 1987. The Chinese hipparion fossils. Palaeont Sin, New Ser C, 25: 1-250 |
| [34] | Rook L, Bernor R L, 2013. Hippotherium malpassii (Equidae, Mammalia) from the latest Miocene (late Messinian; MN13) of Monticino gypsum quarry (Brisighella, Emilia-Romagna, Italy). Boll Soc Paleontol Ital, 52(2): 95-102 |
| [35] | Rook L, Oms O, Benvenuti M et al., 2011. Magnetostratigraphy of the Late Miocene Baccinello-Cinigiano Basin (Tuscany, Italy) and the age of Oreopithecus bambolii faunal assemblages. Palaegeogr Palaeoclimat Palaeoecol, 305: 286-294 |
| [36] | Sefve I, 1927. Die Hipparionen Nord-Chinas. Palaeont Sin, New Ser C, 4(2): 1-93 |
| [37] | Sen S, 1989. Hipparion Datum and its chronologic evidence in the Mediterranean area. In: Lindsay E H, Fahlbusch V, Mein P eds. European Neogene Mammal Chronology. New York: Plenum Press. 495-506 |
| [38] | Sisson S, 1953. The Anatomy of the Domestic Animals. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company. 1-972 |
| [39] | Sun B Y, 2024. Fossil Equidae in the Linxia Basin with biostratigraphic and paleozoogeographic significance. Acta Geol Sin-Engl, 98(1): 1-9 |
| [40] | Sun B Y, Deng T, 2019. The Equus Datum and the Early Radiation of Equus in China. Front Ecol Evol, 7: 429 |
| [41] | Sun B Y, Zhang X X, Liu Y et al., 2018. Sivalhippus ptychodus and Sivalhippus platyodus (Perissodactyla, Mammalia) from the late Miocene of China. Riv Ital Paleontol Stratigr, 124: 1-22 |
| [42] | Sun B Y, Liu Y, Chen S et al., 2022. Hippotherium Datum implies Miocene palaeoecological pattern. Sci Rep, 12: 3605 |
| [43] | Tong H W, 2012. Evolution of the non-Coelodonta dicerorhine lineage in China. C R Palevol, 11: 555-562 |
| [44] | Wang M Y, Wang H Y, Zhu Z X et al., 2021. Late Miocene-Pliocene Asian summer monsoon variability linked to both tropical Pacific temperature and Walker Circulation. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 561: 116823 |
| [45] | Woodburne M O, 2005. A new occurrence of Cormohipparion, with implications for the Old World Hippotherium Datum. J Vert Paleont, 25(1): 256-257 |
| [46] | Woodburne M O, 2007. Phyletic diversification of the Cormohipparion occidentale complex (Mammalia, Perissodactyla, Equidae), Late Miocene, North America, and the origin of the Old World Hippotherium Datum. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist, 306: 1-180 |
| [47] | Woodburne M O, Bernor R L, 1980. On superspecific groups of some Old World hipparionine horses. J Paleontol, 54(6): 1319-1348 |
| [48] | Xue X X, Zhang Y X, Yue L P, 2006. Paleoenvironments indicated by the fossil mammalian assemblages from red clay-Loess sequence in the Chinese Loess Plateau since 8.0 Ma B.P. Sci China Ser D, 49(5): 518-530 |
| [49] | Zdansky O, 1923. Fundorte der Hipparion-Fauna um Pao-Te-Hsien in NW-Shansi. Bull Geol Surv China, 5: 69-81 |
| [50] | Zhang Y X, Xue X X, Yue L P, 1995. Age and division of Neogene “Red Bed” of Laogaochuan, Fugu County, Shaanxi. J Stratigr, 19: 214-219 |
| [51] | Zhang Z Q, Kaakinen A, Liu L P et al., 2013. Chapter 6: Mammalian biochronology of the Late Miocene Bahe Formation. In: Wang X M, Flynn L J, Fortelius M eds. Fossil Mammals of Asia: Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology. New York: Columbia University Press. 187-202 |
| [52] | Zhegallo V I, 1971. Hipparions from the Neogene deposits of Western Mongolia and Tuva. Sovm Sovet-Mongol Nauch-Issled Geol Eksped Tr, 3: 98-119 |
| [53] | Zhu Y M, Zhou L P, Mo D W et al., 2008. A new magnetostratigraphic framework for late Neogene Hipparion Red Clay in the eastern Loess Plateau of China. Palaegeogr Palaeoclimat Palaeoecol, 268: 47-57 |
| [54] | Zouhri S, Bensalmia A, 2005. Révision systématique des Hipparion sensu lato (Perissodactyla, Equidae) de l’Ancien Monde. Estud Geol, 61: 61-99 |
| [1] | 徐光辉, 袁志伟, 任艺, 廖浚伶, 赵丽君, 宋海军. 江苏安徽早三叠世裂齿鱼科一新种:吴氏三叠鱼. 古脊椎动物学报, 2024, 62(3): 165-185. |
| [2] | 薛钦元, 余逸伦, 潘照晖, 朱幼安, 朱敏. 节甲鱼类(有颌脊椎动物干群)系统发育多样性的衰落与泥盆纪重大环境-生物事件耦合. 古脊椎动物学报, 2024, 62(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | 罗彦超, 朱敏, 卢立伍, 潘照晖. 湖南中泥盆统跳马涧组中华沟鳞鱼再研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(4): 261-276. |
| [4] | 冯东昊, 徐光辉, 马昕莹, 任艺. 云贵地区中三叠世近鲱形类贵州中华真颌鱼(Sinoeugnathus kueichowensis)的分类学修订. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(3): 161-181. |
| [5] | 任艺, 徐光辉. 云南罗平中三叠世翼鳕属一新种及早期辐鳍鱼类系统发育关系. 古脊椎动物学报, 2021, 59(3): 169-199. |
| [6] | 肖博, 盛桂莲, 袁俊霞, 王斯人, 胡家铭, 陈顺港, 姬海龙, 侯新东, 赖旭龙. 中国东北鹿亚科动物亚化石的古DNA分子鉴定及系统发育分析. 古脊椎动物学报, 2020, 58(4): 328-337. |
| [7] | 张驰. MrBayes分子钟定年之程序. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(3): 241-252. |
| [8] | 徐光辉, 马昕莹, 吴飞翔, 任艺. 云南中三叠世拱鱼目一新属种及早期铰齿鱼类系统发育关系再评估. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(3): 181-204. |
| [9] | 王敏, 邹晶梅, 周忠和. 孔子鸟目(鸟类:尾综骨类)的分类厘定. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(1): 1-37. |
| [10] | 戎钰芬. 河北围场下白垩统围场皇家螈(Regalerpeton weichangensis) (两栖类:有尾类)的再研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2018, 56(2): 121-136. |
| [11] | 马昕莹, 徐光辉. 云南中三叠世(安尼期)预言鱼目(全骨鱼类:近鲱形类)一新属种. 古脊椎动物学报, 2017, 55(2): 162-176. |
| [12] | 毕丛山,倪喜军,王元青,孟 津,Daniel L. GEBO . 孟氏苏崩猴( 哺乳动物纲:近兔猴超科) 的齿列以及亚洲窃果猴科系统发育关系的再研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2016, 54(3): 181-211. |
| [13] | 董丽萍,Susan E. EVANS,王 原 . 安徽潜山古新世蜥蜴化石的分类学厘定. 古脊椎动物学报, 2016, 54(3): 243-268. |
| [14] | 王健,张兆群. 内蒙古三盛公渐新世古鼬(食肉目,古鼬科)新材料及系统发育关系分析. 古脊椎动物学报, 2015, 53(4): 310-334. |
| [15] | 高红艳,倪喜军. 基干鲸类的多样性及其与中兽和偶蹄类的系统关系. 古脊椎动物学报, 2015, 53(2): 153-176. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||