

古脊椎动物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 181-204.DOI: 10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.190319
徐光辉1,2,*, 马昕莹1,2,3, 吴飞翔1,2, 任艺1,2,3
收稿日期:2019-01-28
出版日期:2019-07-20
发布日期:2019-07-20
通讯作者:
xuguanghui@ivpp.ac.cn基金资助:XU Guang-Hui1,2,*, MA Xin-Ying1,2,3, WU Fei-Xiang1,2, REN Yi1,2,3
Received:2019-01-28
Published:2019-07-20
Online:2019-07-20
摘要:
铰齿鱼类是全骨鱼类中的一支,包括现生的雀鳝及其关系密切的化石类型。产自云贵地区中三叠世安尼期(~244 Ma)地层的拱鱼目(Kyphosichthyiformes)鱼类代表了铰齿鱼类最早的化石记录。根据最近在云南罗平关岭组二段发现的4块保存完好的鱼化石,命名了拱鱼目一个新属种,优美玉带鱼(Yudaiichthys eximius gen. et sp. nov.)。新的发现为重新研究拱鱼目和其他早期铰齿鱼类的系统发育关系提供了契机。分支分析结果表明,过去定义的拱鱼科(Kyphosichthyidae)和圣乔治鱼属(Sangiorgioichthys)都是并系类群。重新厘定后的拱鱼目分为拱鱼科和腊山鱼科(Lashanichthyidae fam. nov.); 其中,拱鱼科包括拱鱼属(Kyphosichthys)和富源鱼属(Fuyuanichthys); 苏氏圣乔治鱼(Sangiorgioichthys sui)和羊圈圣乔治鱼(S. yangjuanensis)归入新建的腊山鱼属(Lashanichthys gen. nov.), 和玉带鱼属一起组成腊山鱼科。圣乔治鱼属被移出拱鱼目,限定于产自圣乔治山地区中三叠世拉丁期地层的两个种(Sangiorgioichthys aldae和S. valmarensis); 该属和更进步的铰齿鱼类(半椎鱼目和雀鳝目)构成姐妹群关系。修订后的分支图为了解铰齿鱼类解剖特征的早期演化历史提供了新的见解。
中图分类号:
徐光辉, 马昕莹, 吴飞翔, 任艺. 云南中三叠世拱鱼目一新属种及早期铰齿鱼类系统发育关系再评估. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(3): 181-204.
XU Guang-Hui, MA Xin-Ying, WU Fei-Xiang, REN Yi. A Middle Triassic kyphosichthyiform from Yunnan, China, and phylogenetic reassessment of early ginglymodians. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2019, 57(3): 181-204.
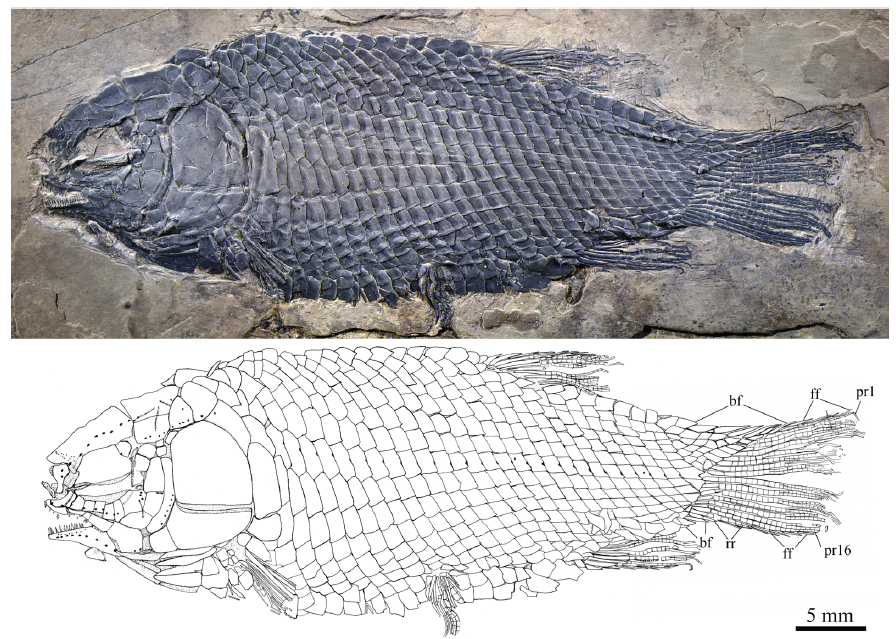
Fig. 1 Holotype of Yudaiichthys eximius gen. et sp. nov., IVPP V 20431 Abbreviations: bf. basal fulcrum; ff. fringing fulcrum; pr. principal fin ray; rr. rudimentary ray
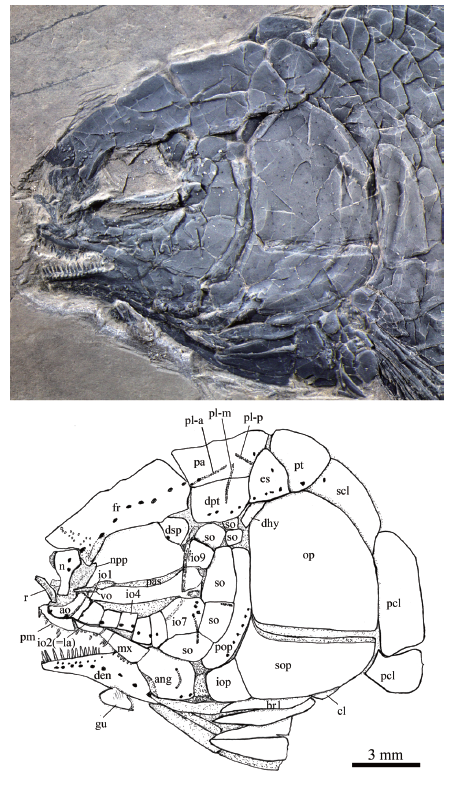
Fig. 4 Skull and pectoral girdle of Yudaiichthys eximius gen. et sp. nov., IVPP V 20431 Abbreviations: ang. angular; ao. antorbital; br. branchiostegal rays; cl. cleithrum; den. dentary;dhy. dermohyal; dpt. dermopterotic; dsp. dermosphenotic; es. extrascapular; fr. frontal; gu. gular;io. infraorbital; iop. interopercle; la. lacrimal; mx. maxilla; n. nasal; npp. nasal process of premaxilla;op. opercle; pa. parietal; pas. parasphenoid; pcl. postcleithrum; pl-a. anterior pit-line; pl-m. middle pit-line; pl-p. posterior pit-line; pm. premaxilla; pop. preopercle; pt. posttemporal; qj. quadratojugal; r. rostral;scl. supracleithrum; so. suborbital; sop. subopercle; su. supraorbital; vo. Vomer
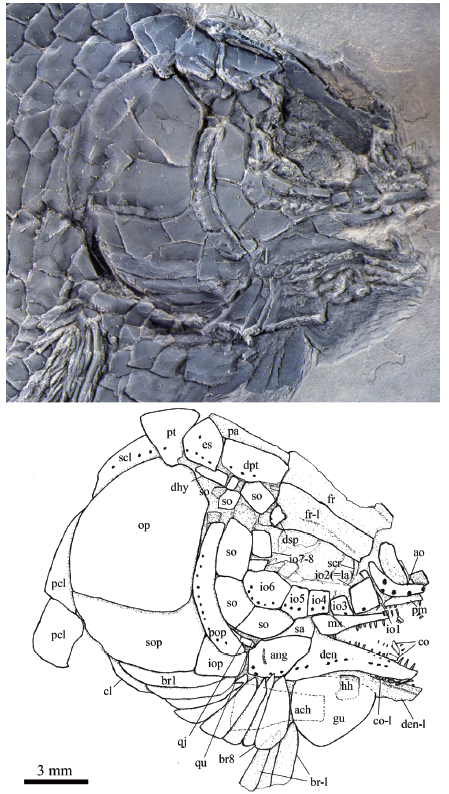
Fig. 6 Skull and pectoral girdle of Yudaiichthys eximius gen. et sp. nov., IVPP V 20434 Abbreviations: ach. anterior ceratohyal; co. coronoid; hh. hypohyal; qu. quadrate; sa. supra-angular;scr. sclerotic ring. For other abbreviations see Fig. 4
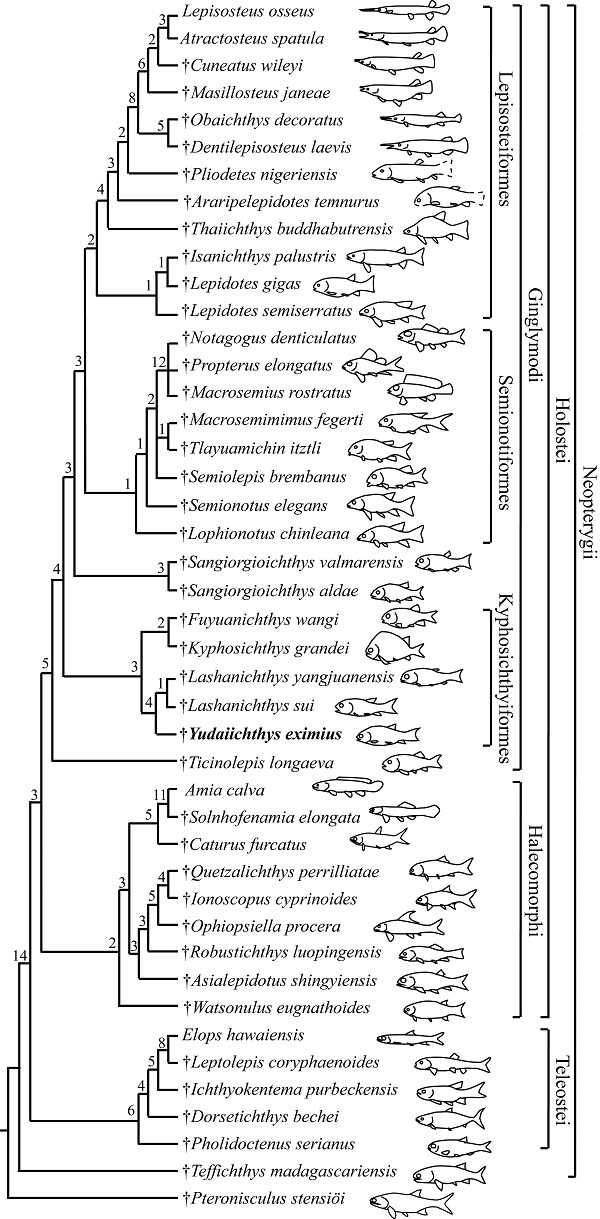
Fig. 8 Strict consensus of five most parsimonious trees (TL= 521, CI= 0.4760, RI= 0.7509), illustrating the phylogenetic position of Yudaiichthys within the Neopterygii Digits above nodes indicate Bremer decay indices
| [1] |
Alvarado-Ortega J, Espinosa-Arrubarrena L, 2008. A new genus of ionoscopiform fish (Halecomorphi) from the Lower Cretaceous (Albian) lithographic limestones of the Tlayúa quarry, Puebla, Mexico. J Paleont, 82:163-175
DOI URL |
| [2] | Arratia G, 2013. Morphology, taxonomy, and phylogeny of Triassic pholidophorid fishes (Actinopterygii, Teleostei). Soc Vert Paleont Mem (Suppl J Vert Paleont), 13: 1-138 |
| [3] | Bartram A W H, 1977. The Macrosemiidae, a Mesozoic family of holostean fishes. Bull Br Mus Geol, 29:137-234 |
| [4] |
Benton M J, Zhang Q Y, Hu S X et al., 2013. Exceptional vertebrate biotas from the Triassic of China, and the expansion of marine ecosystems after the Permo-Triassic mass extinction. Earth Sci Rev, 125:199-243
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Brito P M, Alvarado-Ortega J, Meunier F J, 2017. Earliest known lepisosteoid extends the range of anatomically modern gars to the Late Jurassic. Sci Rep, 7:17830
DOI URL |
| [6] | Bürgin T, 2004. †Eosemionotus ceresiensis sp. nov., a new semionotiform fish (Actinopetygii, Halecostomi) from the Middle Triassic of Monte San Giorgio (southern Switzerland). In: Arratia G, Tintori A eds. Mesozoic Fishes 3 - Systematics, Pleoenvironments and Biodiversity. Munich: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. 239-251 |
| [7] |
Cavin L, 2010. Diversity of Mesozoic semionotiform fishes and the origin of gars (Lepisosteidae). Naturwissenschaften, 97:1035-1040
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Cavin L, Suteethorn V, 2006. A new Semionotiform (Actinopterygii, Neopterygii) from Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous deposits of North-East Thailand, with comments on the relationships of Semionotiforms. Palaeontology, 49:339-353
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Cavin L, Deesri U, Suteethorn V, 2013. Osteology and relationships of Thaiichthys nov. gen.: a Ginglymodi from the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous of Thailand. Palaeontology, 56:183-208
DOI URL |
| [10] | Cavin L, Deesri U, Veran M et al., 2018. A new Lepisosteiformes (Actinopterygii: Ginglymodi) from the Early Cretaceous of Laos and Thailand, SE Asia. J Syst Palaeont, doi: 10.1080/14772019.2018.1426060 |
| [11] | Chen W Q, Sun Z Y, Tintori A et al., 2014. A new species of Sangiorgioichthys Tintori & Lombardo, 2007 (Actinopterygii; Semionotiformes) from the Pelsonian (Anisian, Middle Triassic) of Guizhou Province, South China. Neues Jahrb Geol Paläont, Abh, 273:65-74 |
| [12] | Cope E D, 1872. Observations on the systematic relations of the fishes. Proc Am Assoc Adv Sci, 20:317-343 |
| [13] | Deesri U, Lauprasert K, Suteethorn V et al., 2014. A new species of the ginglymodian fish Isanichthys from the Late Jurassic Phu Kradung Formation, northeastern Thailand. Acta Palaeont Pol, 59:313-331 |
| [14] |
Deesri U, Jintasakul P, Cavin L, 2016. A new Ginglymodi (Actinopterygii, Holostei) from the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous of Thailand, with comments on the early diversification of Lepisosteiformes in Southeast Asia. J Vert Paleont, 36:e1225747
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Drucker E G, Lauder G V, 2002. Wake dynamics and locomotor function in fishes: interpreting evolutionary patterns in pectoral fin design. Integr Comp Biol, 42:997-1008
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Ebert M, 2018. Cerinichthys koelblae, gen. et sp. nov., from the Upper Jurassic of Cerin, France, and its phylogenetic setting, leading to a reassessment of the phylogenetic relationships of Halecomorphi (Actinopterygii). J Vert Paleont, 38:e1420071
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Gibson S Z, 2013a. A new hump-backed ginglymodian fish (Neopterygii, Semionotiformes) from the Upper Triassic Chinle Formation of southeastern Utah. J Vert Paleont, 33:1037-1050
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Gibson S Z, 2013b. Biodiversity and evolutionary history of †Lophionotus (Neopterygii: †Semionotiformes) from the western United States. Copeia, 2013:582-603
DOI URL |
| [19] | Grande L, 2010. An empirical synthetic pattern study of gars (Lepisosteiformes) and closely related species, based mostly on skeletal anatomy. The resurrection of Holostei. Copeia, 10(Suppl):1-871 |
| [20] | Grande L, Bemis W E, 1998. A comprehensive phylogenetic study of amiid fishes (Amiidae) based on comparative skeletal anatomy: an empirical search for interconnected patterns of natural history. Soc Vert Paleont Mem (Suppl J Vert Paleont), 4: 1-690 |
| [21] |
Hu S X, Zhang Q Y, Chen Z Q et al., 2011. The Luoping biota: exceptional preservation, and new evidence on the Triassic recovery from end-Permian mass extinction. Proc R Soc B, 278:2274-2282
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lin H Q, Sun Z Y, Tintori A et al., 2011. A new species of Habroichthys Brough, 1939 (Actinopterygii; Peltopleuriformes) from the Pelsonian (Anisian, Middle Triassic) of Yunnan Province, South China. Neues Jahrb Geol Paläont, Abh, 262:79-89 |
| [23] | Lombardo C, Tintori A, 2008. A new semionotid fish (Actinopterygii) from the Upper Triassic of northern Italy. In: Arratia G, Schultze H P, Wilson M V H eds. Mesozoic Fishes - Homology and Phylogeny. Munich: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. 129-142 |
| [24] | Lombardo C, Sun Z Y, Tintori A et al., 2011. A new species of the genus Perleidus (Actinopterygii: Perleidiformes) from the Middle Triassic of southern China. Boll Soc Paleont Ital, 50:75-83 |
| [25] | Lombardo C, Tintori A, Tona D, 2012. A new species of Sangiorgioichthys (Actinopterygii, Semionotiformes) from the Kalkschieferzone of Monte San Giorgio (Middle Triassic; Meride, Canton Ticino, Switzerland). Boll Soc Paleont Ital, 51:203-212 |
| [26] |
López-Arbarello A, 2012. Phylogenetic interrelationships of ginglymodian fishes (Actinopterygii: Neopterygii). PLoS ONE, 7:e39370
DOI URL |
| [27] |
López-Arbarello A, Alvarado-Ortega J, 2011. New semionotiform (Neopterygii) from the Tlayúa Quarry (Early Cretaceous, Albian), Mexico. Zootaxa, 2749:1-24
DOI URL |
| [28] |
López-Arbarello A, Sferco E, 2018. Neopterygian phylogeny: the merger assay. R Soc Open Sci, 5:172337
DOI URL |
| [29] |
López-Arbarello A, Wencker L C M, 2016. New callipurbeckiid genus (Ginglymodi: Semionotiformes) from the Tithonian (Late Jurassic) of Canjuers, France. Paläont Z, 90:543-560
DOI URL |
| [30] |
López-Arbarello A, Sun Z Y, Sferco E et al., 2011. New species of Sangiorgioichthys Tintori and Lombardo, 2007 (Neopterygii, Semionotiformes) from the Anisian of Luoping (Yunnan Province, South China). Zootaxa, 2749:25-39
DOI URL |
| [31] |
López-Arbarello A, Burgin T, Furrer H et al., 2016. New holostean fishes (Actinopterygii: Neopterygii) from the Middle Triassic of the Monte San Giorgio (Canton Ticino, Switzerland). PeerJ, 4:e2234
DOI URL |
| [32] | Ma X Y, Xu G H, 2017. A new ionoscopiform fish (Holostei: Halecomorphi) from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Yunnan, China. Vert PalAsiat, 55:92-106 |
| [33] | Maisey J G, 1991. Araripelepidotes Silva Santos, 1985. In: Maisey J G ed. Santana Fossils: an Illustrated Atlas. Neptune, NJ: TFH Publications Inc. 118-123 |
| [34] | Müller J, 1844. Über den Bau und die Grenzen der Ganoiden, und über das natürliche System der Fische. Ber Akad Wiss Berlin, 1844:416-422 |
| [35] |
Near T J, Eytan R I, Dornburg A et al., 2012. Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification. Proc Nat Acad Sci, 109:13698-13703
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Olsen P E, McCune A R, 1991. Morphology of the Semionotus elegans species group from the Early Jurassic part of the Newark Supergroup of eastern North America with comments on the family Semionotidae (Neopterygii). J Vert Paleont, 11:269-292
DOI URL |
| [37] | Patterson C, 1973. Interrelationships of holosteans. In: Greenwood P H, Miles R S, Patterson C eds. Interrelationships of Fishes. Zool J Linn Soc, 53(Suppl):233-305 |
| [38] |
Patterson C, 1982. Morphology and interrelationships of primitive actinopterygian fishes. Am Zool, 22:241-259
DOI URL |
| [39] | Regan C T, 1923. The skeleton of Lepidosteus, with remarks on the origin and evolution of the lower neopterygian fishes. Proc Zool Soc London, 1923: 445-461 |
| [40] |
Ruehl C B, Shervette V, Dewitt T J, 2011. Replicated shape variation between simple and complex habitats in two estuarine fishes. Biol J Linn Soc, 103:147-158
DOI URL |
| [41] | Schaeffer B, Dunkle D, 1950. A semionotid fish from the Chinle Formation, with considerations of its relationships. Am Mus Novit, 1457:1-29 |
| [42] |
Schröder K M, López-Arbarello A, Ebert M, 2012. Macrosemimimus gen. nov. (Actinopterygii, Semionotiformes) from the Late Jurassic of Germany, England and France. J Vert Paleont, 32:512-529
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Schultze H P, Möller H, 1986. Wirbeltierreste aus dem Mittleren Muschelkalk (Trias) von Göttingen, West-Deutschland. Paläont Z, 60:109-129
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Sun Z Y, Ni P G, 2018. Revision of Kyphosichthys grandei Xu & Wu, 2012 from the Middle Triassic of Yunnan Province, South China: implications for phylogenetic interrelationships of ginglymodian fishes. J Syst Palaeont, 16:67-85
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Sun Z Y, Tintori A, Jiang D Y et al., 2009. A new perleidiform (Actinopterygii, Osteichthyes) from the middle Anisian (Middle Triassic) of Yunnan, South China. Acta Geol Sin, 83:460-470
DOI URL |
| [46] | Sun Z Y, Lombardo C, Tintori A et al., 2012. Fuyuanperleidus dengi Geng et al. 2012 (Osteichthyes, Actinopterygii) from the Middle Triassic of Yunnan Province, South China. Riv Ital Paleont Stratigr, 118:359-373 |
| [47] |
Sun Z Y, Lombardo C, Tintori A et al., 2015. A new species of Altisolepis (Peltopleuriformes, Actinopterygii) from the Middle Triassic of southern China. J Vert Paleont, 35:e909819
DOI URL |
| [48] | Sun Z Y, Tintori A, Lombardo C et al., 2016. New miniature neopterygians from the Middle Triassic of Yunnan Province, South China. Neues Jahrb Geol Paläont, Abh, 282:135-156 |
| [49] | Swofford D L, 2003. PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4.0b10. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates |
| [50] | Tan K, Jin F, 2013. Re-study on Gymnoichthys inopinatus from Middle Triassic of Luoping, Yunnan, China. Vert PalAsiat, 51:1-16 |
| [51] | Tintori A, Lombardo C, 2007. A new early Semionotidae (Semionotiformes, Actinopterygii) from the upper Ladinian of Monte San Giorgio area (southern Switzerland and northern Italy). Riv Ital Paleont Stratigr, 113:369-381 |
| [52] | Tintori A, Sun Z Y, Lombardo C et al., 2007. New specialized basal neopterygians (Actinopterygii) from Triassic of the Tethys Realm. Geol Insubr, 10:13-20 |
| [53] | Tintori A, Sun Z Y, Lombardo C et al., 2010. A new basal neopterygian from the Middle Triassic of Luoping County (South China). Riv Ital Paleont Stratigr, 116:161-172 |
| [54] | Wen W, Zhang Q Y, Hu S X et al., 2012. A new genus of basal actinopterygian fish from the Anisian (Middle Triassic) of Luoping, Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Acta Palaeont Pol, 57:149-160 |
| [55] | Wen W, Zhang Q Y, Hu S X et al., 2013. Coelacanths from the Middle Triassic Luoping Biota, Yunnan, South China, with the earliest evidence of ovoviviparity. Acta Palaeont Pol, 58:175-193 |
| [56] | Wen W, Hu S X, Zhang Q Y et al., 2018. A new species of Platysiagum from the Luoping Biota (Anisian, Middle Triassic, Yunnan, South China) reveals the relationship between Platysiagidae and Neopterygii. Geol Mag, doi: 10.1017/S0016756818000079 |
| [57] | Wenz S, 1967. Compléments à l’étude des poisons Actinoptérygiens du Jurassique français. Paris: Centre National de la Recherché Scientifique. 1-276 |
| [58] | Wenz S, 1999. †Pliodetes nigeriensis, gen. nov. et. sp. nov., a new semionotid fish from the Lower Cretaceous of Gadoufaoua (Niger Republic): phylogenetic comments. In: Arratia G, Schultze H P eds. Mesozoic Fishes 2 - Systematics and Fossil Record. München: Verlag Dr. Friederich Pfeil. 107-120 |
| [59] | Westoll T S, 1944. The Haplolepidae, a new family of Late Carboniferous bony fishes - a study in taxonomy and evolution. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist, 83:1-121 |
| [60] |
Wu F X, Sun Y L, Hao W C et al., 2009. New species of Saurichthys (Actinopterygii: Saurichthydae) from Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Yunnan Province, China. Acta Geol Sin, 83:440-450
DOI URL |
| [61] | Wu F X, Sun Y L, Xu G H et al., 2011. New saurichthyid actinopterygian fishes from the Anisian (Middle Triassic) of southwestern China. Acta Palaeont Pol, 56:581-614 |
| [62] | Wu F X, Sun Y L, Fang G Y, 2018. A new species of Saurichthys from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of southwestern China. Vert Palasiat, 56:273-294 |
| [63] |
Xu G H, Ma X Y, 2016. A Middle Triassic stem-neopterygian fish from China sheds new light on the peltopleuriform phylogeny and internal fertilization. Sci Bull, 61:1766-1774
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Xu G H, Ma X Y, 2018. Redescription and phylogenetic reassessment of Asialepidotus shingyiensis (Holostei: Halecomorphi) from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of China. Zool J Lin Soc, 184:95-114
DOI URL |
| [65] | Xu G H, Shen C C, 2015. Panxianichthys imparilis gen. et sp. nov., a new ionoscopiform (Halecomorphi) from the Middle Triassic of Guizhou, China. Vert PalAsiat, 53:1-15 |
| [66] |
Xu G H, Wu F X, 2012. A deep-bodied ginglymodian fish from the Middle Triassic of eastern Yunnan Province, China, and the phylogeny of lower neopterygians. Chin Sci Bull, 57:111-118
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Xu G H, Zhao L J, 2016. A Middle Triassic stem-neopterygian fish from China shows remarkable secondary sexual characteristics. Sci Bull, 61:338-344
DOI URL |
| [68] | Xu G H, Shen C C, Zhao L J, 2014a. Pteronisculus nielseni sp. nov., a new stem-actinopteran fish from the Middle Triassic of Luoping, Yunnan Province, China. Vert Palasiat, 52:364-380 |
| [69] |
Xu G H, Zhao L J, Coates M I, 2014b. The oldest ionoscopiform from China sheds new light on the early evolution of halecomorph fishes. Biol Lett, 10:20140204
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Xu G H, Ma X Y, Ren Y, 2018a. Fuyuanichthys wangi gen. et sp. nov. from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of China highlights the early diversification of ginglymodian fishes. PeerJ, 6:e6054
DOI URL |
| [71] | Xu G H, Ma X Y, Zhao L J, 2018b. A large peltopleurid fish from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of Yunnan and Guizhou, China. Vert PalAsiat, 56:106-120 |
| [72] |
Zhang Q Y, Zhou C Y, Lü T et al., 2009. A conodont-based Middle Triassic age assignment for the Luoping Biota of Yunnan, China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 52:1673-1678
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王维, 雷洪, 李淳. 云南中三叠世一恐头龙科小型主龙型类. 古脊椎动物学报, 2024, 62(1): 13-32. |
| [2] | 薛钦元, 余逸伦, 潘照晖, 朱幼安, 朱敏. 节甲鱼类(有颌脊椎动物干群)系统发育多样性的衰落与泥盆纪重大环境-生物事件耦合. 古脊椎动物学报, 2024, 62(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | 罗彦超, 朱敏, 卢立伍, 潘照晖. 湖南中泥盆统跳马涧组中华沟鳞鱼再研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(4): 261-276. |
| [4] | 冯东昊, 徐光辉, 马昕莹, 任艺. 云贵地区中三叠世近鲱形类贵州中华真颌鱼(Sinoeugnathus kueichowensis)的分类学修订. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(3): 161-181. |
| [5] | 尚庆华, 李淳, 王维. 云南罗平中三叠世安尼期鳍龙类Nothosaurus一新种. 古脊椎动物学报, 2022, 60(4): 249-270. |
| [6] | 任艺, 徐光辉. 云南罗平中三叠世翼鳕属一新种及早期辐鳍鱼类系统发育关系. 古脊椎动物学报, 2021, 59(3): 169-199. |
| [7] | 肖博, 盛桂莲, 袁俊霞, 王斯人, 胡家铭, 陈顺港, 姬海龙, 侯新东, 赖旭龙. 中国东北鹿亚科动物亚化石的古DNA分子鉴定及系统发育分析. 古脊椎动物学报, 2020, 58(4): 328-337. |
| [8] | 徐光辉. 贵州中三叠世兴义生物群卢加诺鱼属(卢加诺鱼科,新鳍鱼类)一新种. 古脊椎动物学报, 2020, 58(4): 267-282. |
| [9] | Torsten M. SCHEYER, 王维, 李淳, Feiko MIEDEMA, Stephan N. F. SPIEKMAN. 中国中三叠世富源巨胫龙(主龙型小纲,长颈龙科)的骨骼学再描述. 古脊椎动物学报, 2020, 58(3): 169-187. |
| [10] | 张驰. MrBayes分子钟定年之程序. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(3): 241-252. |
| [11] | 廖俊棋, 徐星. 意外北票龙(兽脚类:镰刀龙类)头部骨骼学研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(2): 117-132. |
| [12] | 王敏, 邹晶梅, 周忠和. 孔子鸟目(鸟类:尾综骨类)的分类厘定. 古脊椎动物学报, 2019, 57(1): 1-37. |
| [13] | 吴飞翔,孙元林,房庚雨. 我国西南地区中三叠世安尼期龙鱼属(Saurichthys)一新种. 古脊椎动物学报, 2018, 56(4): 273-294. |
| [14] | 戎钰芬. 河北围场下白垩统围场皇家螈(Regalerpeton weichangensis) (两栖类:有尾类)的再研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2018, 56(2): 121-136. |
| [15] | 尚庆华 ,李 淳,吴肖春. 纤细滇美龙(Dianmeisaurus gracilis Shang & Li, 2015)新材料. 古脊椎动物学报, 2017, 55(2): 145-161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||