

古脊椎动物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (1): 19-26.DOI: 10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.201126
邱铸鼎1(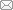 ), 王晓鸣1,4(
), 王晓鸣1,4( ), 李强1, 李录1, 王洪江2, 陈海峰3
), 李强1, 李录1, 王洪江2, 陈海峰3
收稿日期:2020-07-10
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-20
通讯作者:
qiuzhuding@ivpp.ac.cn;基金资助:
QIU Zhu-Ding1( ), WANG Xiao-Ming1,4(
), WANG Xiao-Ming1,4( ), LI Qiang1, LI Lu1, WANG Hong-Jiang2, CHEN Hai-Feng3
), LI Qiang1, LI Lu1, WANG Hong-Jiang2, CHEN Hai-Feng3
Received:2020-07-10
Published:2021-01-20
Online:2021-01-20
摘要:
过去40年,在内蒙古中部地区的陆相新近纪化石地点中应用了筛选技术,采集到大量标本,这些发现迅速填补着晚新生代动物群演替和生物年代学认识的空白。在把孤立的化石组合按时代先后进行排序和建立动物群序列框架中,小哺乳动物的发现和研究发挥了至关重要的作用。报道了另一个产自哈拉津胡舒地点的晚中新世动物群,这个动物群再次展示了蒙古高原上令人“叹为观止”的化石种类和丰度。新地点位于该地区的最北部,并为玄武岩所覆盖,产出的标本计有7000余件,代表大、小哺乳动物达63种。虽然这一动物群混杂了少量下部层位的属种,但它不失为内蒙古中部地区一个较为真实地反映晚中新世小哺乳动物组成和生态环境的动物群。初步分析表明,哈拉津胡舒动物群属中国陆生哺乳动物年代的晚中新世早期的灞河期,可能比阿木乌苏动物群稍晚,但比沙拉动物群略早。
中图分类号:
邱铸鼎, 王晓鸣, 李强, 李录, 王洪江, 陈海峰. 内蒙古哈拉津胡舒晚中新世动物群. 古脊椎动物学报, 2021, 59(1): 19-26.
QIU Zhu-Ding, WANG Xiao-Ming, LI Qiang, LI Lu, WANG Hong-Jiang, CHEN Hai-Feng. Late Miocene mammalian fauna of Halajin Hushu in Nei Mongol, China. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2021, 59(1): 19-26.
Fig. 2 Map of Abag Volcanic Field showing contact relationships of Neogene sediments and capping basalts The Halajin Hushu locality is the northern-most fossil site associated with basalts. Only one fossil site is shown for each formations or beds that contain a discrete fauna. Cenozoic exposures and basalts are drawn from satellite images in Google Earth Pro (Version 7.3.3.7699) (2020), as is the inset (upper right) with semitransparent color enhancements of basal and Cenozoic exposures
| Taxa | N | Taxa | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eulipotyphla | Zapodidae | |||
| Erinaceidae | Parasminthus tangingoli* | 11 | ||
| Mioechinus? gobiensis | 1142 | P. parvulus* | 5 | |
| Erinaceus sp. | 2 | Eozapus major | 13 | |
| Talpidae | Sinozapus parvus | 264 | ||
| Yanshuella cf. Y. primaeva | 117 | Sicista sp. | 257 | |
| Quyania cf. Q. chowi | 52 | Heterosminthus orientalis | 931 | |
| Desmanella storchi | 155 | Lophocricetus xianensis | 1119 | |
| Talpinae indet. | 41 | Zapodidae indet. 1 | 17 | |
| Soricidae | Zapodidae indet. 2 | 7 | ||
| Mongolosorex sp. | 2 | Dipodidae | ||
| Sorex cf. S. minutoides | 12 | Protalactaga lantianensis | 4 | |
| Sorex ertemteensis | 128 | Paralactaga shalaensis | 4 | |
| Petenyia cf. P. katrinae | 28 | Cricetidae | ||
| Cokia kowalskae | 19 | Alloeumyarion sp.* | 3 | |
| Paranourosorex cf. P. inexspectatus | 171 | Democricetodon lindsayi | 8 | |
| Paenelimnoecus obtusus | 2 | Plesiodipus leei* | 10 | |
| Soricidae indet. | 2 | P. progressus | 7 | |
| Chiroptera | P. robustus | 4 | ||
| Chiroptera indet. | 1 | Gobicricetodon robustus | 5 | |
| Rodentia | Gobicricetodon aff. G. flynni | 3 | ||
| Ctenodactylidae | Khanomys baii | 72 | ||
| Tataromys sp.* | 2 | Colloides xiaomingi | 8 | |
| Aplodontidae | Colloides sp. nov. | 35 | ||
| Ansomys borealis | 9 | Kowalskia shalaensis | 233 | |
| A. lophodens | 21 | Microtoscoptes sp. | 1 | |
| Pseudaplodon amuwusuensis | 1 | Ischymomys sp. | 2 | |
| Sciuridae | Epimeriones sp. nov. | 116 | ||
| Tamias ertemtensis | 339 | Baranomyinae indet. | 98 | |
| Spermophilinus sp. | 13 | Spalacidae | ||
| Atlantoxerus sp. | 5 | Pararhizomys qinensis | 3 | |
| Prospermophilus orientalis | 76 | Gerbillidae | ||
| Hylopetes sp. | 3 | Myocricetodon sp.* | 3 | |
| Gliridae | Myospalacidae | |||
| Orientiglis wuae | 227 | Prosiphneus qiui | 199 | |
| Eomyidae | Lagomorpha | |||
| Leptodontomys gansus | 405 | Ochotonidae | ||
| L. lii | 52 | Desmatolagus sp. | 23 | |
| Keramidomys fahlbuschi | 41 | Ochotona sp. | 364 | |
| K. magnus | 254 | Artiodactyla | ||
| Castoridae | Moschidae | |||
| Monosaulax tungurensis | 10 | Moschidae indet. | 15 | |
| Castor sp. | 1 |
Table 1 Taxa and specimen number (N) of the Halajin Hushu assemblage
| Taxa | N | Taxa | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eulipotyphla | Zapodidae | |||
| Erinaceidae | Parasminthus tangingoli* | 11 | ||
| Mioechinus? gobiensis | 1142 | P. parvulus* | 5 | |
| Erinaceus sp. | 2 | Eozapus major | 13 | |
| Talpidae | Sinozapus parvus | 264 | ||
| Yanshuella cf. Y. primaeva | 117 | Sicista sp. | 257 | |
| Quyania cf. Q. chowi | 52 | Heterosminthus orientalis | 931 | |
| Desmanella storchi | 155 | Lophocricetus xianensis | 1119 | |
| Talpinae indet. | 41 | Zapodidae indet. 1 | 17 | |
| Soricidae | Zapodidae indet. 2 | 7 | ||
| Mongolosorex sp. | 2 | Dipodidae | ||
| Sorex cf. S. minutoides | 12 | Protalactaga lantianensis | 4 | |
| Sorex ertemteensis | 128 | Paralactaga shalaensis | 4 | |
| Petenyia cf. P. katrinae | 28 | Cricetidae | ||
| Cokia kowalskae | 19 | Alloeumyarion sp.* | 3 | |
| Paranourosorex cf. P. inexspectatus | 171 | Democricetodon lindsayi | 8 | |
| Paenelimnoecus obtusus | 2 | Plesiodipus leei* | 10 | |
| Soricidae indet. | 2 | P. progressus | 7 | |
| Chiroptera | P. robustus | 4 | ||
| Chiroptera indet. | 1 | Gobicricetodon robustus | 5 | |
| Rodentia | Gobicricetodon aff. G. flynni | 3 | ||
| Ctenodactylidae | Khanomys baii | 72 | ||
| Tataromys sp.* | 2 | Colloides xiaomingi | 8 | |
| Aplodontidae | Colloides sp. nov. | 35 | ||
| Ansomys borealis | 9 | Kowalskia shalaensis | 233 | |
| A. lophodens | 21 | Microtoscoptes sp. | 1 | |
| Pseudaplodon amuwusuensis | 1 | Ischymomys sp. | 2 | |
| Sciuridae | Epimeriones sp. nov. | 116 | ||
| Tamias ertemtensis | 339 | Baranomyinae indet. | 98 | |
| Spermophilinus sp. | 13 | Spalacidae | ||
| Atlantoxerus sp. | 5 | Pararhizomys qinensis | 3 | |
| Prospermophilus orientalis | 76 | Gerbillidae | ||
| Hylopetes sp. | 3 | Myocricetodon sp.* | 3 | |
| Gliridae | Myospalacidae | |||
| Orientiglis wuae | 227 | Prosiphneus qiui | 199 | |
| Eomyidae | Lagomorpha | |||
| Leptodontomys gansus | 405 | Ochotonidae | ||
| L. lii | 52 | Desmatolagus sp. | 23 | |
| Keramidomys fahlbuschi | 41 | Ochotona sp. | 364 | |
| K. magnus | 254 | Artiodactyla | ||
| Castoridae | Moschidae | |||
| Monosaulax tungurensis | 10 | Moschidae indet. | 15 | |
| Castor sp. | 1 |

Fig. 3 Stratigraphic section of Halajin Hushu A. photograph of Halajin Hushu section (photo looking southward and taken on August 4, 2015 by X. Wang); B. closeup of exposures at fossiliferous horizon and a nodular zone immediately above (photo looking eastward and taken on June 18, 2018 by X. Wang); C. measured section of Halajin Hushu strata
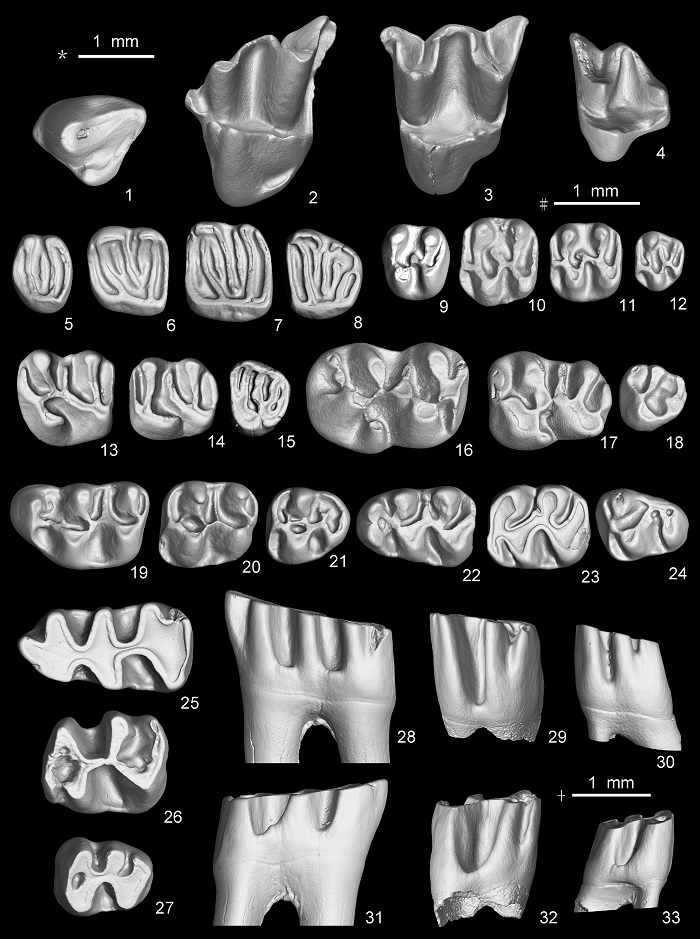
Fig. 4 Selected specimens of small mammals from Halajin Hushu Yanshuella cf. Y. primaeva (1-4), left P4-M3; Orientiglis wuae (5-8), left P4-M3; Leptodontomys gansus (9-12), left P4-M3; Eozapus major (13-15), right M1-M2 (reversed) and left M3; Lophocricetus xianensis (16-18), left M1-M3; Kowalskia shalaensis (19-21), left M1-M3; Colloides sp. nov. (22-24), left m1-m3; Epimeriones sp. nov. (25-33), left m1-m3; 1-27. occlusal view, 28-30. lingual view, 31-33. buccal view; scales: * for 1-4, # for 5-24, + for 25-33

Fig. 5 Selected specimens of moschids, Moschidae indet. from Halajin Hushu Left upper molar (1-3), right upper molar (4-6), left m1/2 (7-9), right p4 (10-12), partial right p3 (13-15), and right p2 (16-18); 1, 4, 7, 12, 15, 18. buccal views; 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17. occlusal views; 3, 6, 9, 10, 13, 16. lingual views
| 1 |
Aiglstorfer M, Mayda S, Heizmann E P J , 2018. First record of late Middle Miocene Moschidae from Turkey: Micromeryx and Hispanomeryx from Catakbağyaka (Muğla, SW Turkey). C R Palevol, 17(3):178-188
DOI URL |
| 2 | Bohlin B , 1946. The fossil mammals from the Tertiary deposit of Taben-buluk, western Kansu. Part 2: Simplicidentata, Carnivora, Artiodactyla and Primates. Palaeont Sin, New Ser C, 8B:1-259 |
| 3 |
Chen M, Niu F, Liu Q Y et al., 2015. Mantle-driven uplift of Hangai Dome: new seismic constraints from adjoint tomography. Geophys Res Lett, 42(17):6967-6974
DOI URL |
| 4 | Chen S S, Fan Q C, Zhao Y W et al., 2013. Geochemical characteristics of basalts in Bilike area and its geological significance, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol Sin, 29(8):2695-2708 |
| 5 | Daxner-Hock G , 1972. Die Wirbeltierfauna aus dem Alt-Pliozan (Pont) vom Eichkogel bei Modling (Niederosterreich). IV. Gerbillinae (Rodentia, Mammalia). Ann Naturhist Mus Wien, 76:143-150 |
| 6 | Daxner-Höck G, Höck E , 2015. Catalogus fossilium Austriae. - 4. Rodentia neogenica. Wien: Verlag Österreichischen Akademie Wissenschaften. 1-158 |
| 7 |
Deng F L, Macdougall J D , 1992. Proterozoic depletion of the lithosphere recorded in mantle xenoliths from Inner Mongolia. Nature, 360:333-336
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Deng T, Wang H J, Wang X M et al., 2016. The Late Miocene Hipparion (Equidae, Perissodactyla) fossils from Baogeda Ula, Inner Mongolia, China. Hist Biol, 28(1-2):53-68
DOI URL |
| 9 | Devyatkin Y V, Smelov S B , 1980. Position of basalts in the Cenozoic sedimentary sequence of Mongolia. Intern Geol Rev, 22(3):307-317 |
| 10 | Engesser B , 1972. Die Obermiozane Säugetierfauna von Anwil (Baselland). Tätigkeitsber Naturforsch Ges Basell, 28:35-363 |
| 11 | Fahlbusch V, Qiu Z D, Storch G , 1983. Neogene mammalian faunas of Ertemte and Harr Obo in Nei Monggol, China. - 1. Report on field work in 1980 and preliminary results. Sci Sin, Ser B, 26(2):205-224 |
| 12 | Fejfar O , 1999. Microtoid cricetids. In: Rößner G E, Heißig K eds. The Miocene Land Mammals of Europe. München: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil. 365-372 |
| 13 | Gong L W, Li N, Fan Q C et al., 2016. Mapping the topography and cone morphology of the Dalinor volcanic swarm in Inner Mongolia with remote sensing and DEM data. Front Earth Sci, 10(3):578-594 |
| 14 | Google Earth Pro ( Version 7.3.3 . 7699), 2020. Available from https://www.google.com/work/earthmaps/earthpro.html. Mountain View, CA: Google Inc |
| 15 |
He J, Wu Q , 2020. Mantle transition zone structure beneath the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Sci China Earth Sci, 63(4):548-560
DOI URL |
| 16 |
He J, Wu Q, Sandvol E et al., 2016. The crustal structure of south central Mongolia using receiver functions. Tectonics, 35(6):1392-1403
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Ho K S, Liu Y A N, Chen J C et al., 2008. Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of late Cenozoic Abaga basalts, Inner Mongolia: implications for petrogenesis and mantle process. Geochem J, 42(4):339-357
DOI URL |
| 18 | Huang X S , 1992. Zapodidae (Rodentia, Mammalia) from the Middle Oligocene of Ulantatal, Nei Mongol. Vert PalAsiat, 30(4):249-286 |
| 19 |
Kaakinen A, Abdul Aziz H, Passey B H et al., 2015. Age and stratigraphic context of Pliopithecus and associated fauna from Miocene sedimentary strata at Damiao, Inner Mongolia, China. J Asian Earth Sci, 100:78-90
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Kröner A, Kovach V, Belousova E et al., 2014. Reassessment of continental growth during the accretionary history of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Res, 25(1):103-125
DOI URL |
| 21 | Li Q , 2010. Pararhizomys (Rodentia, Mammalia) from the Late Miocene of Baogeda Ula, central Nei Mongol. Vert PalAsiat, 48(1):48-62 |
| 22 | Li Q, Wang X M, Qiu Z D , 2003. Pliocene mammalian fauna of Gaotege in Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia), China. Vert PalAsiat, 41(2):104-114 |
| 23 | Liu R X, Chen W J, Sun J Z et al., 1992. The K-Ar age and tectonic environment of Cenozoic rock in China. In: Liu R X ed. The Age and Geochemistry of Cenozoic Volcanic Rock in China. Beijing: Seismic Press. 1-43 |
| 24 | Luo X Q, Chen Q T , 1990. Preliminary study on geochronology for Cenozoic basalts from Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol Mineral, 9(1):37-46 |
| 25 | McKenna M C, Bell S K , 1997. Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level. New York: Columbia University Press. 1‒631 |
| 26 | Meng J, Wang B Y, Bai Z Q , 1996. A new middle Tertiary mammalian locality from Sunitezuoqi, Nei Mongol. Vert PalAsiat, 34(4):297-304 |
| 27 | Mennecart B, Aiglstorfer M, Göhlich U et al., 2019. On the oldest Mongolian moschids (Mammalia, Ruminantia) and the early moschid evolution. Palaeontol Electron, 22.2. 53A:1-17 |
| 28 |
Ni X J, Qiu Z D , 2002. The micromammalian fauna from the Leilao, Yuanmo hominoid locality: implications for biochronology and paleoecology. J Hum Evol, 42:535-546
DOI URL |
| 29 | Qiu Z D , 1996. Middle Miocene micromammalian fauna from Tunggur, Nei Mongol. Beijing: Science Press. 1-216 |
| 30 | Qiu Z D , 2001a. Cricetid rodents from the Middle Miocene Quantougou Fauna of Lanzhou, Gansu. Vert PalAsiat, 39(3):204-214 |
| 31 | Qiu Z D , 2001b. Glirid and gerbillid rodents from the Middle Miocene Quantougou Fauna of Lanzhou, Gansu. Vert PalAsiat, 39(4):297-305 |
| 32 | Qiu Z D , 2010. Cricetid rodents from the Early Miocene Xiacaowan Formation, Sihong, Jiangsu. Vert PalAsiat, 48(1):27-47 |
| 33 | Qiu Z D, Li Q , 2008. Late Miocene micromammals from the Qaidam Basin in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Vert PalAsiat, 46(4):284-306 |
| 34 | Qiu Z D, Li Q , 2016. Neogene rodents from central Nei Mongol, China. Palaeont Sin, New Ser C, 30:1-684 |
| 35 |
Qiu Z D, Storch G , 2000. The Early Pliocene micromammalian fauna of Bilike, Inner Mongolia, China (Mammalia: Lipotyphla, Chiroptera, Rodentia, Lagomorpha). Senckenbergiana Lethaea, 80(1):173-229
DOI URL |
| 36 | Qiu Z D, Wang X M , 1999. Small mammal faunas and their ages in Miocene of central Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia). Vert PalAsiat, 37(2):120-139 |
| 37 | Qiu Z D, Zheng S H, Zhang Z Q , 2004a. Murids from the Late Miocene Bahe Formation, Lantian, Shaanxi. Vert PalAsiat, 42(1):67-76 |
| 38 | Qiu Z D, Zheng S H, Zhang Z Q , 2004b. Gerbillids from the Late Miocene Bahe Formation, Lantian, Shaanxi. Vert PalAsiat, 42(3):193-204 |
| 39 | Qiu Z D, Wang X M, Li Q , 2006. Faunal succession and biochronology of the Miocene through Pliocene in Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia). Vert PalAsiat, 44(2):164-181 |
| 40 | Qiu Z D, Wang X M, Li Q , 2013. Neogene faunal succession and biochronology of central Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia). In: Wang X M, Flynn L J, Fortelius M eds. Fossil Mammals of Asia - Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology. New York: Columbia University Press. 155-186 |
| 41 | Qiu Z X, Yan D F, Chen G F et al., 1988. Preliminary report on the field work in 1986 at Tung-gur, Nei Mongol. Chinese Sci Bull, 33(5):399-404 |
| 42 | Qiu Z X, Qiu Z D, Deng T et al., 2013. Neogene land mammal stages/ages of China: toward the goal to establish an Asian land mammal stage/age scheme. In: Wang X M, Flynn L J, Fortelius M eds. Fossil Mammals of Asia - Neogene Biostratigraphy and Chronology. New York: Columbia University Press. 29-90 |
| 43 | Sánchez I M, Morales J , 2006. Distribución biocronológica de los Moschidae (Mammalia, Ruminantia) en España. Estud Geol, 62(1):533-545 |
| 44 |
Sánchez I M, Domingo M S, Morales J , 2010. The genus Hispanomeryx (Mammalia, Ruminanta, Moschidae) and its bearing on musk deer phylogeny and systematics. Palaeontology, 53(5):1023-1047
DOI URL |
| 45 |
Sánchez I M, Demiguel D, Quiralte V et al., 2011. The first known Asian Hispanomeryx (Mammalia, Ruminantia, Moschidae). J Vert Paleont, 31(6):1397-1403
DOI URL |
| 46 | Schlosser M , 1924. Tertiary vertebrates from Mongolia. Palaeont Sin, Ser C, 1:1-132 |
| 47 | Shao J, Ji J Q, Lu F X et al., 2008. Response of the continental lithosphere to the spreading mechanism: space-time distribution of the Meso-Cenozoic volcanic activities in the Liao-Meng geological corridor, China. Geol Bull China, 27(9):1431-1440 |
| 48 | Storch G, Qiu Z D , 1983. The Neogene mammalian faunas of Ertemte and Harr Obo in Inner Mongolia (Nei Mongol), China. - 2. Moles - Insectivora: Talpidae. Senckenbergiana Lethaea, 64(2/4):89-127 |
| 49 |
Sukselainen L, Kaakinen A, Zhang Z Q et al., 2017. The palaeoenvironment of the Middle Miocene pliopithecid locality in Damiao, Inner Mongolia, China. J Hum Evol, 108:31-46
DOI URL PMID |
| 50 |
Sun L, Deng C L, Wang X M et al., 2018. Magnetostratigraphic dating of the Late Miocene Baogeda Ula Formation and associated fauna in central Inner Mongolia, northern China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol, 505:243-255
DOI URL |
| 51 | Teilhard de Chardin P , 1926. Déscription de mammifères Tertiaires de Chine et de Mongolie. Ann Paléont, 15:1-52 |
| 52 | Topachevsky V A, Skorik A F, Rekovec L I , 1978. The most ancient voles of the Miocrotini tribe (Rodentia, Microtidae) from the South of the Ukrainian SSR. Kiev Vestn Zool, 1978: 35-41 |
| 53 |
Tseng Z J, Wang X M , 2007. The first record of the Late Miocene Hyaenictitherium hyaenoides Zdansky (Carnivora: Hyaenidae) in Inner Mongolia and an evaluation of the genus. J Vert Paleont, 27(3):699-708
DOI URL |
| 54 | Vislobokova I A, Lavrov A V , 2009. The earliest musk deer of the genus Moschus and their significance in clarifying of evolution and relationships of the family Moschidae. Paleontol J, 43:87-99 |
| 55 | Wang B Y, Qiu Z X , 2018. Late Miocene pararhizomyines from Linxia Basin of Gansu, China. Palaeont Sin, New Ser C, 31:1-271 |
| 56 |
Wang S Q, Shi Q Q, Hui Z C et al., 2015. Diversity of Moschidae (Ruminantia, Artiodactyla, Mammalia) in the Middle Miocene of China. Paleontol Res, 19(2):143-155
DOI URL |
| 57 | Wang X M, Li P , 2011. A new fossil site with a re-worked Paleogene assemblage at Baogeda Ula, central Nei Mongol. Vert PalAsiat, 49(1):114-122 |
| 58 | Wang X M, Qiu Z D, Li Q et al., 2009. A new Early to Late Miocene fossiliferous region in central Nei Mongol: lithostratigraphy and biostratigraphy in Aoerban strata. Vert PalAsiat, 47(2):111-134 |
| 59 | Wang X M, Tseng Z J, Takeuchi G T , 2012. Zoogeography, molecular divergence, and the fossil record - the case of an extinct fisher, Pekania palaeosinensis (Mustelidae, Mammalia), from the Late Miocene Baogeda Ula Formation, Inner Mongolia. Vert PalAsiat, 50(3):293-307 |
| 60 | Whitford-Stark J L , 1987. A survey of Cenozoic volcanism on mainland Asia. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap, 213:1-74 |
| 61 |
Windley B F, Allen M B , 1993. Mongolian plateau: evidence for a late Cenozoic mantle plume under central Asia. Geology, 21(4):295-298
DOI URL |
| 62 |
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J et al., 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J Geol Soc, 164(1):31-47
DOI URL |
| 63 | Wu W Y, Meng J, Ye J et al., 2009. The Miocene mammals from Dingshanyanchi Formation of North Junggar Basin, Xinjiang. Vert PalAsiat, 47(3):208-233 |
| 64 |
Zhang M L, Guo Z F , 2016. Origin of late Cenozoic Abaga-Dalinuoer basalts, eastern China: implications for a mixed pyroxenite-peridotite source related with deep subduction of the Pacific slab. Gondwana Res, 37:130-151
DOI URL |
| 65 | Zhang Z Q, Flynn L J, Qiu Z D , 2005. New materials of Pararhizomys from northern China. Palaeontol Electron, 8(1), 5A:1-9 |
| 66 | Zhang Z Q, Wang L H, Liu Y et al., 2011. Miocene mammalian faunal succession from Damiao, central Nei Mongol and the environmental changes. Quat Sci, 31(4):608-613 |
| 67 | Zheng S H, Zhang Z Q , 2000. Late Miocene-Early Pleistocene micromammals from Wenwanggou of Lingtai, Gansu, China. Vert PalAsiat, 38(1):58-71 |
| 68 | Zhou Z , 1984. Late Middle Miocene mammalian fauna from Amuwusu, Inner Mongolia. Master’s thesis. Beijing: Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. 1-37 |
| [1] | 劳伦斯J.弗林, 李强, 吉学平, 王晓鸣. 云南晚中新世一巨型竹鼠. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(4): 277-283. |
| [2] | 王伴月, 邱占祥. 甘肃临夏盆地牙沟地区椒子沟组底部的小哺乳动物化石. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(4): 284-316. |
| [3] | 王伴月, 邱占祥, 王世骐. 甘肃临夏盆地椒子沟组上部满散村小哺乳动物群. 古脊椎动物学报, 2023, 61(2): 123-141. |
| [4] | 张立民, 董为, 倪喜军, 李强. 晚中新世晚期土城子小哺乳动物组合及土城子动物群在内蒙古中部地区新近纪哺乳动物群序列中的位置. 古脊椎动物学报, 2021, 59(1): 45-63. |
| [5] | Leena SUKSELAINEN,Hannele PELTONEN,Anu KAAKINEN,张兆群. 内蒙古大庙中新世小哺乳动物化石埋藏学研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2017, 55(1): 71-88. |
| [6] | 李永项,胡松梅,王社江,张云翔. 陕西洛南龙牙洞小哺乳动物化石新材料. 古脊椎动物学报, 2016, 54(4): 332-350. |
| [7] | 白 滨,王 旭. 小哺乳动物化石牙齿釉质碳、氧同位素测试方法简介及应用前景. 古脊椎动物学报, 2013, 51(3): 242-251. |
| [8] | 张颖奇,严亚玲,刘毅弘,魏光飚. 几何形态测量学方法在小哺乳动物化石分类鉴定中的应用—— 4种?类化石大样本的个案研究. 古脊椎动物学报, 2012, 50(4): 361-372. |
| [9] | 王元青,孟 津,金 迅. 内蒙古二连盆地古近系研究回顾及存在问题. 古脊椎动物学报, 2012, 50(3): 181-203. |
| [10] | 王晓鸣,邱铸鼎,李强,富田幸光,木村由莉,曾志杰,王洪江. 内蒙古中部敖尔班地区的岩石及生物地层. 古脊椎动物学报, 2009, 47(2): 111-134. |
| [11] | 邱铸鼎 , 李强. 青海柴达木盆地晚中新世深沟小哺乳动物群. 古脊椎动物学报, 2008, 46(4): 284-306. |
| [12] | 蔡保全 , 郑绍华 , 李 强. 蔚县盆地牛头山(铺路)剖面晚上新世/早更新世小哺乳动物. 古脊椎动物学报, 2007, 45(3): 232-245. |
| [13] | 郑绍华,蔡保全,李强. 泥河湾盆地洞沟剖面上新世/更新世小哺乳动物. 古脊椎动物学报, 2006, 44(04): 320-331. |
| [14] | 张兆群, 郑绍华, 刘建波. 泥河湾盆地上新世小哺乳动物生物地层学及相关问题讨论. 古脊椎动物学报, 2003, 41(04): 306-313. |
| [15] | 张兆群, 郑绍华. 甘肃灵台小石沟晚中新世——上新世小哺乳动物生物地层. 古脊椎动物学报, 2001, 39(01): 54-66. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||