

Vertebrata Palasiatica ›› 2024, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (3): 165-185.DOI: 10.19615/j.cnki.2096-9899.240528
XU Guang-Hui1(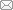 ), YUAN Zhi-Wei2, REN Yi1,3, LIAO Jun-Ling4, ZHAO Li-Jun5, SONG Hai-Jun2
), YUAN Zhi-Wei2, REN Yi1,3, LIAO Jun-Ling4, ZHAO Li-Jun5, SONG Hai-Jun2
Received:2024-01-28
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-08-13
徐光辉1( ), 袁志伟2, 任艺1,3, 廖浚伶4, 赵丽君5, 宋海军2
), 袁志伟2, 任艺1,3, 廖浚伶4, 赵丽君5, 宋海军2
作者简介:xuguanghui@ivpp.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
XU Guang-Hui, YUAN Zhi-Wei, REN Yi, LIAO Jun-Ling, ZHAO Li-Jun, SONG Hai-Jun. Teffichthys wui sp. nov., a new perleidid fish from the Early Triassic of Jiangsu and Anhui, China. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2024, 62(3): 165-185.
徐光辉, 袁志伟, 任艺, 廖浚伶, 赵丽君, 宋海军. 2024, 62(3): 165-185, 江苏安徽早三叠世裂齿鱼科一新种:吴氏三叠鱼. 古脊椎动物学报.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.vertpala.ac.cn/EN/10.19615/j.cnki.2096-9899.240528
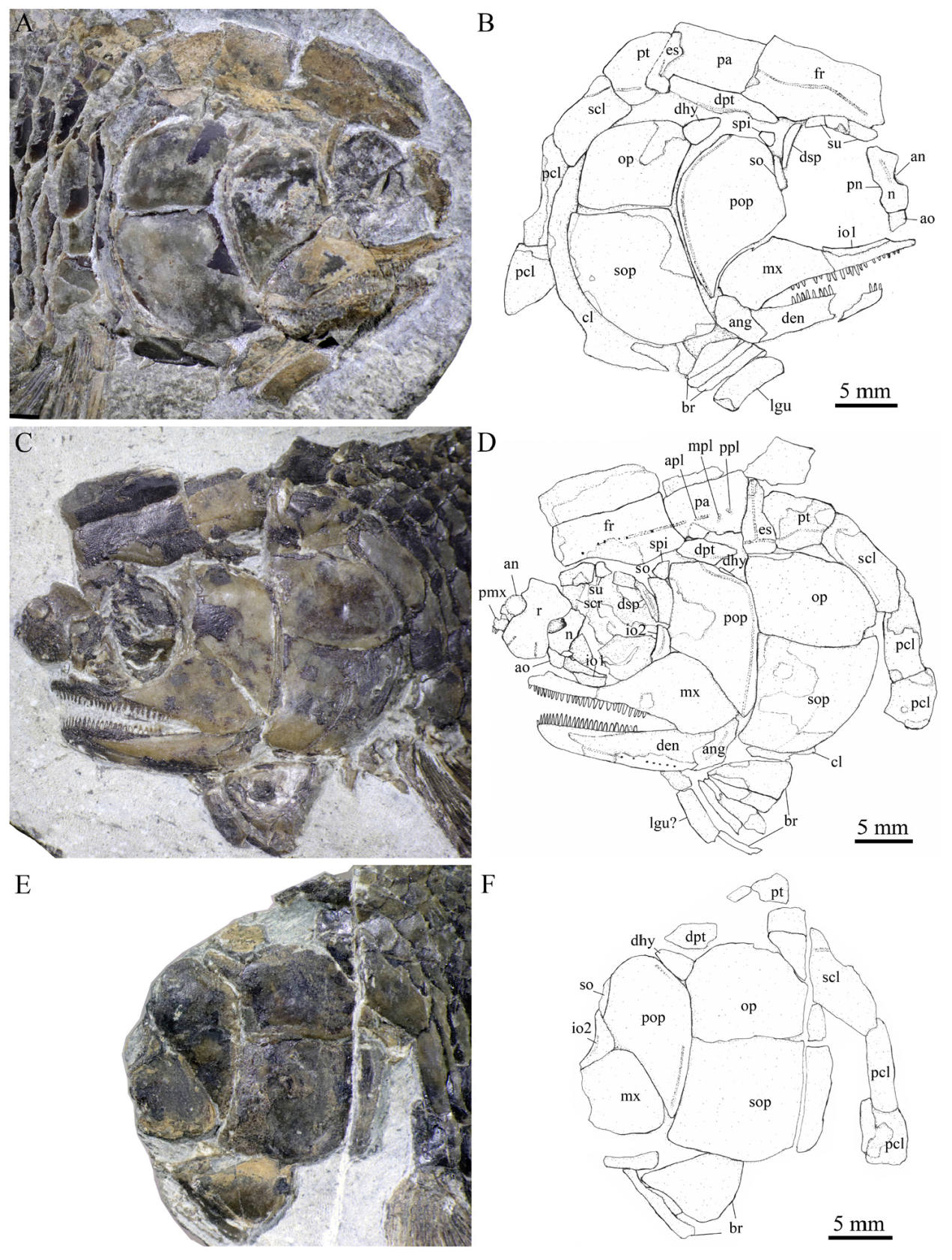
Fig. 3 Photographs (A, C, E) and line-drawings (B, D, F) of skull and pectoral girdle of Teffichthys wui sp. nov. from Jurong, Jiangsu A, B. IVPP V27614; C, D. IVPP V30880; E, F. IVPP V30881
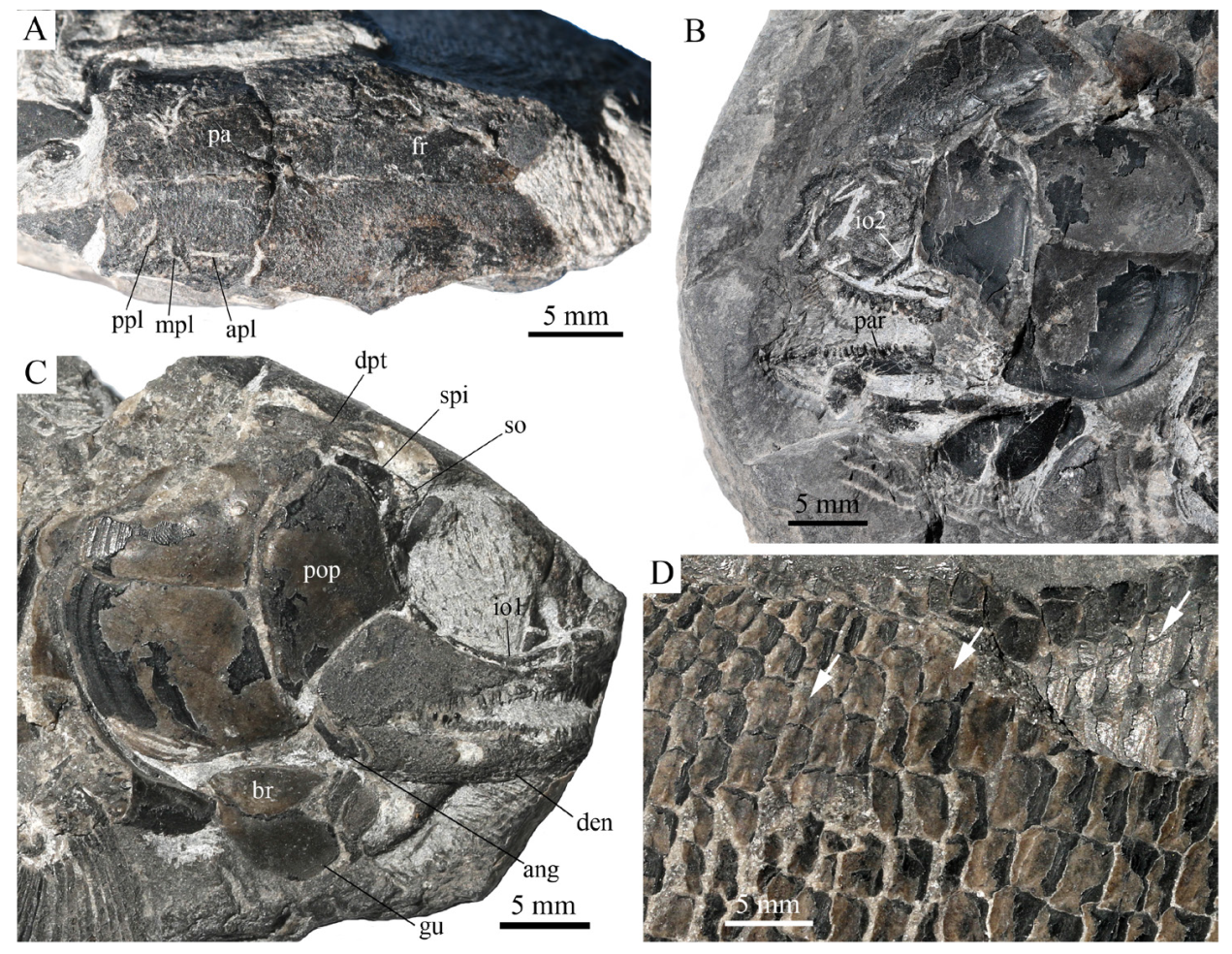
Fig. 4 Skull and scales of Teffichthys wui sp. nov. from Chaohu, Anhui A, C. skull of CUGM J2202 in dorsal (A) and right lateral (C) view; B. skull of CUGM J2201 in left lateral view; D. CUGM J2202, anterior flank scales, with arrows indicating the dorsal peg of the scale
Fig. 6 Fins and scales of Teffichthys wui sp. nov. from Jurong, Jiangsu A. pectoral fin, IVPP V30880; B. anal fin, IVPP V30881; C, D, E. IVPP V27614: caudal fin (C), dorsal fin (D), and anal fin (E)
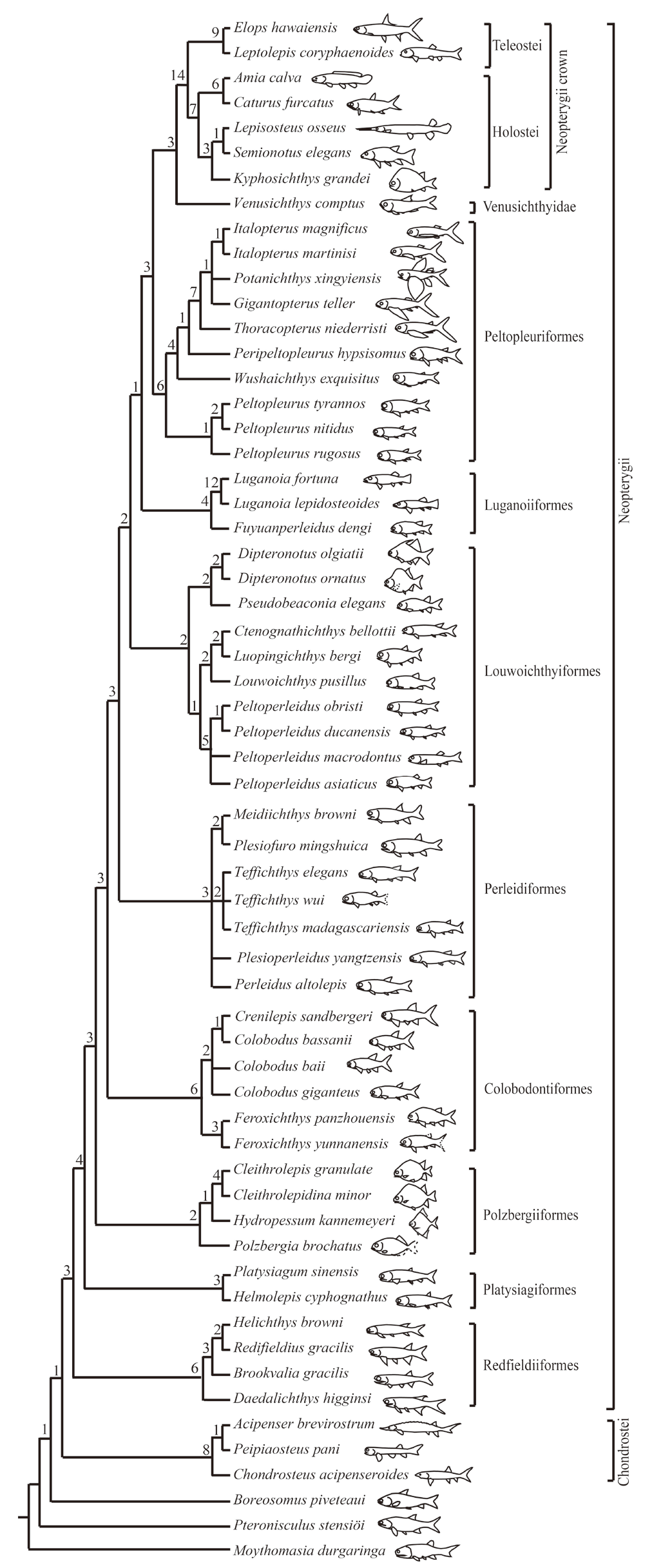
Fig. 7 Strict consensus of 468 most parsimonious trees Tree length = 427 steps, consistency index = 0.4496, retention index = 0.7777, illustrating the phylogenetic position of Teffichthys wui sp. nov. within the Neopterygii. Digits above nodes indicate Bremer decay indices
| Order | Family | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Redfieldiiformes Berg, 1940 | Redfieldiidae Berg, 1940; Brookvaliidae Berg, 1940; Schizurichthyidae Hutchinson, | supraorbital canal reaching dermopterotic; orbit bordered anteriorly by adnasal (supraorbital) and premaxilla-antorbital; one or two pairs of branchiostegal rays |
| Platysiagiformes Brough, | Platysiagidae Brough, | nasals joined in midline; absence of suborbital and supraorbital bones; maxilla slender with numerous tiny pointed teeth |
| Polzbergiiformes Griffith, | Polzbergiidae Griffith, Cleithrolepididae Wade, 1935; Hydropessidae Hutchinson, | maxilla ending below posterior orbital margin; teeth reduced or lost in both jaws; body deep, with marked dorsal hump; scales deep, ornamented with fine tubercles or rugae |
| Colobodontiformes ord. nov. | Colobodontidae Andersson, 1916 | subopercle with deep anterodorsal process; multiple supraorbitals arranged in more than one horizontal rows; absence of suborbitals; ganoid tubercles on caudal fin rays |
| Perleidiformes Berg, | Perleididae Brough, | preopercle/maxilla contact nearly equal to anterior margin of subopercle in length; suborbital/preopercle contact nearly half length of anterior margin of preopercle; supracleithrum longer than posterior margin of opercle |
| Louwoichthyiformes Xu, | Louwoichthyidae Xu, Peltoperleididae Xu, Pseudobeaconiidae López-Arbarello & Zavattieri, | maxilla relatively short and deep, ending at level of posterior orbital margin; ventral portion of preopercle contacting maxilla anteriorly; subopercle slightly larger than opercle, with prominent anteroventral extension; two or three pairs of branchiostegal rays |
| Luganoiiformes Lehman, 1958 | Luganoiidae Brough, Fuyuanperleididae Sun et al., 2012 | lacrimal fused with maxilla; anterior flank scales greatly deepened, contacting two or three horizontal rows of posterior scales; absence of fringing fulcra |
| Peltopleuriformes Gardiner, 1967 | Peltopleuridae Brough, Thoracopteridae Griffith, | supraorbital sensory canal ending in the frontal; absence of preopercle/dermopterotic contact; presence of postspiracle; enlarged lateral scutes associated with anal fin; brush-like rays proximally articulating several stout segments at posterior portion of male anal fin |
| Venusichthyidae Xu & Zhao, | absence of supraorbitals; oral margin of maxilla convex; two preopercular elements on each side of skull; quadratomandibular articulation below orbital center; two pairs of branchiostegal rays; hook-like contact organ anterior to male anal fin |
Table 1 Characteristics of main stem neopterygian clades
| Order | Family | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Redfieldiiformes Berg, 1940 | Redfieldiidae Berg, 1940; Brookvaliidae Berg, 1940; Schizurichthyidae Hutchinson, | supraorbital canal reaching dermopterotic; orbit bordered anteriorly by adnasal (supraorbital) and premaxilla-antorbital; one or two pairs of branchiostegal rays |
| Platysiagiformes Brough, | Platysiagidae Brough, | nasals joined in midline; absence of suborbital and supraorbital bones; maxilla slender with numerous tiny pointed teeth |
| Polzbergiiformes Griffith, | Polzbergiidae Griffith, Cleithrolepididae Wade, 1935; Hydropessidae Hutchinson, | maxilla ending below posterior orbital margin; teeth reduced or lost in both jaws; body deep, with marked dorsal hump; scales deep, ornamented with fine tubercles or rugae |
| Colobodontiformes ord. nov. | Colobodontidae Andersson, 1916 | subopercle with deep anterodorsal process; multiple supraorbitals arranged in more than one horizontal rows; absence of suborbitals; ganoid tubercles on caudal fin rays |
| Perleidiformes Berg, | Perleididae Brough, | preopercle/maxilla contact nearly equal to anterior margin of subopercle in length; suborbital/preopercle contact nearly half length of anterior margin of preopercle; supracleithrum longer than posterior margin of opercle |
| Louwoichthyiformes Xu, | Louwoichthyidae Xu, Peltoperleididae Xu, Pseudobeaconiidae López-Arbarello & Zavattieri, | maxilla relatively short and deep, ending at level of posterior orbital margin; ventral portion of preopercle contacting maxilla anteriorly; subopercle slightly larger than opercle, with prominent anteroventral extension; two or three pairs of branchiostegal rays |
| Luganoiiformes Lehman, 1958 | Luganoiidae Brough, Fuyuanperleididae Sun et al., 2012 | lacrimal fused with maxilla; anterior flank scales greatly deepened, contacting two or three horizontal rows of posterior scales; absence of fringing fulcra |
| Peltopleuriformes Gardiner, 1967 | Peltopleuridae Brough, Thoracopteridae Griffith, | supraorbital sensory canal ending in the frontal; absence of preopercle/dermopterotic contact; presence of postspiracle; enlarged lateral scutes associated with anal fin; brush-like rays proximally articulating several stout segments at posterior portion of male anal fin |
| Venusichthyidae Xu & Zhao, | absence of supraorbitals; oral margin of maxilla convex; two preopercular elements on each side of skull; quadratomandibular articulation below orbital center; two pairs of branchiostegal rays; hook-like contact organ anterior to male anal fin |
| [1] | Arratia G, 1999. The monophyly of Teleostei and stem-group teleosts. Consensus and disagreements. In: ArratiaG, Schultze H P eds. Fishes 2 - Systematics and Fossil Record. München: Verlag Dr. 265-334 |
| [2] | Benton M J, Zhang Q Y, Hu S X et al., 2013. Exceptional vertebrate biotas from the Triassic of China, and the expansion of marine ecosystems after the Permo-Triassic mass extinction. Earth Sci Rev, 125: 199-243 |
| [3] | Berg L S, 1937. A classification of fish-like vertebrates. Bull Acad Sci URSS, 4: 1277-1280 |
| [4] | Brough J, 1931. The Triassic fishes of the Karroo System and some general considerations on the bony fishes of the Triassic period. Proc Zool Soc London, 1931: 235-296 |
| [5] | Brough J, 1939. The Triassic Fishes of Besano, Lombardy. London: British Museum (Natural History). 1-117 |
| [6] | Bürgin T, 1992. Basal ray-finned fishes (Osteichthyes; Actinopterygii) from the Middle Triassic of Monte San Giorgio (Canton Tessin, Switzerland). Schweiz Paläont Abh, 114: 1-164 |
| [7] | Bürgin T, 1996. Diversity in the feeding apparatus of perleidid fishes (Actinopterygii) from the Middle Triassic of Monte San Giorgio (Switzerland). In: ArratiaG, ViohlG eds. Mesozoic Fishes and Paleoecology. München: Verlag Dr. 555-565 |
| [8] | Cartanyà J, Fortuny J, Bolet A et al., 2015. Colobodus giganteus (Beltan, 1972) comb. nov. from the Upper Muschelkalk facies of Catalonia (NE Iberian Peninsula). Neues Jahrb Geol Paläont Abh, 278: 323-333 |
| [9] |
Cavin L, 2010. Diversity of Mesozoic semionotiform fishes and the origin of gars (Lepisosteidae). Naturwissenschaften, 97: 1035-1040
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Chen Z Q, Benton M J, 2012. The timing and pattern of biotic recovery following the end-Permian mass extinction. Nat Geosci, 5: 375-383 |
| [11] | Clarke J T, Friedman M, 2018. Body-shape diversity in Triassic-Early Cretaceous neopterygian fishes: sustained holostean disparity and predominantly gradual increases in teleost phenotypic variety. Paleobiology, 44: 402-433 |
| [12] | Coates M I, 1999. Endocranial preservation of a Carboniferous actinopterygian from Lancashire, UK, and the interrelationships of primitive actinopterygians. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B, 354: 435-462 |
| [13] | Cope E D, 1887. Zittel’s manual of palaeontology. Am Nat, 21: 1014-1019 |
| [14] |
Dai X, Davies J, Yuan Z W et al., 2023. A Mesozoic fossil lagerstätte from 250.8 million years ago shows a modern-type marine ecosystem. Science, 379: 567-572
DOI PMID |
| [15] | De Alessandri G, 1910. Studii sui pesci triasici della Lombardia. Mem Soc Ital Sci Nat, 7: 1-147 |
| [16] | Deecke W, 1889. Ueber Fische aus verschiedenen Horizonten der Trias. Palaeontographica, 35: 97-138 |
| [17] | Gardiner B G, 1984. The relationships of the palaeoniscid fishes, a review based on new specimens of Mimia and Moythomasia from the Upper Devonian of Western Australia. Bull Br Mus Nat Hist Geol, 37: 173-428 |
| [18] | Gardiner B G, Schaeffer B, 1989. Interrelationships of lower actinopterygian fishes. Zool J Linn Soc, 97: 135-187 |
| [19] | Geng B H, Jin F, Wu F X et al., 2012. New perleidid fishes from the Middle Triassic strata of Yunnan Province. Geol Bull China, 31: 915-927 |
| [20] | Grande L, 2010. An empirical synthetic pattern study of gars (Lepisosteiformes) and closely related species, based mostly on skeletal anatomy. The resurrection of Holostei. Am Soc Herp Spec Pub, 6: 1-871 |
| [21] | Grande L, Bemis W E, 1998. A comprehensive phylogenetic study of amiid fishes (Amiidae) based on comparative skeletal anatomy: an empirical search for interconnected patterns of natural history. Mem Soc Vert Paleont, 4: 1-690 |
| [22] | Griffith J, 1977. The Upper Triassic fishes from Polzberg bei Lunz, Austria. Zool J Linn Soc, 60: 1-93 |
| [23] | Hurley I A, Mueller R L, Dunn K A et al., 2007. A new time-scale for ray-finned fish evolution. Proc R Soc B, 274: 489-498 |
| [24] | Hutchinson P, 1973. A revision of the redfieldiiform and perleidiform fishes from the Triassic of Bekker’s Kraal (South Africa) and Brookvale (New South Wales). Bull Br Mus Nat Hist (Geol), 22: 235-354 |
| [25] | Jin F, Wang N Z, Cai Z Q, 2003. A revision of the perleidid fishes from the Lower Yangtze region of south China-second report on the fish sequence study near the Permian-Triassic boundary in south China. Vert PalAsiat, 41: 169-184 |
| [26] | Lehman J P, 1952. Étude complémentaire des poissions de l’Eotrias de Madagascar. Kungl Svenska Vetenska Handl Ser 4, 2: 1-201 |
| [27] | Lin H Q, Sun Z Y, Tintori A et al., 2011. A new species of Habroichthys Brough, 1939 (Actinopterygii; Peltopleuriformes) from the Pelsonian (Anisian, Middle Triassic) of Yunnan Province, South China. Neues Jahrb Geol Paläont Abh, 262: 79-89 |
| [28] | Liu G B, Feng H Z, Wang J X et al., 2002. Early Triassic fishes from Jurong, Jiangsu. Acta Palaeont Sin, 41(1): 27-52 |
| [29] | Liu S, Sun Z Y, Ji C et al., 2020. Conodont biostratigraphy and age of the Early Triassic fish-bearing-nodule levels from Nanjing and Jurong, Jiangsu Province, South China. J Earth Sci, 31: 9-22 |
| [30] | Lombardo C, 2001. Actinopterygians from the Middle Triassic of northern Italy and Canton Ticino (Switzerland): anatomical descriptions and nomenclatural problems. Riv Ital Paleont Stratigr, 107: 345-369 |
| [31] | Lombardo C, Sun Z Y, Tintori A et al., 2011. A new species of the genus Perleidus (Actinopterygii: Perleidiformes) from the Middle Triassic of southern China. Boll Soc Paleontol Ital, 50: 75-83 |
| [32] | López-Arbarello A, Zavattieri A M, 2008. Systematic revision of Pseudobeaconia Bordas, 1944, and Mendocinichthys Whitley, 1953 (Actinopterygii: ‘Perleidiformes’) from the Triassic of Argentina. Palaeontology, 51: 1025-1052 |
| [33] | Ma X Y, Xu G H, Geng B H, 2021. Feroxichthys panzhouensis sp. nov., a hump-backed colobodontid (Neopterygii, Actinopterygii) from the early Middle Triassic of Panzhou, Guizhou, China. PeerJ, 9: e11257 |
| [34] | Marramà G, Lombardo C, Tintori A et al., 2017. Redescription of ‘ Perleidus ’ (Osteichthyes, Actinopterygii) from the Early Triassic of northwestern Madagascar. Riv Ital Paleont Stratigr, 123: 219-242 |
| [35] | Mutter R I, 2004. The “perleidiform” family colobodontidae:a review. In: ArratiaG, Mesozoic Fishes 3 - Systematics, Paleoenvironments and Biodiversity. F. Pfeil.Tintori A eds.eds. München: Verlag Dr. 197-208 |
| [36] | Neuman A G, Mutter R J, 2005. Helmolepis cyphognathus , sp. nov., a new platysiagid actinopterygian from the Lower Triassic Sulphur Mountain Formation (British Columbia, Canada). Can J Earth Sci, 42: 25-36 |
| [37] | Nielsen E, 1949. Studies on Triassic fishes from East Greenland. II. Australosomus and Birgeria . Medd Grønland, 146: 1-309 |
| [38] | Nixon K C, 2002. WinClada, version 1.00.08. Available at http://www.cladistics.com |
| [39] | Patterson C, 1973. Interrelationships of holosteans. In: GreenwoodP H, MilesR S,Patterson C eds.eds. Interrelationships of Fishes. London: Academic Press. 233-305 |
| [40] | Piveteau J, 1934. Paléontologie de Madagascar XXI. Les poissons du Trias inférieur. Contribution à l’étude des actinopterygiens. Ann Paléontol, 23: 81-180 |
| [41] | Qian M P, Zhu S P, Zhao F M et al., 1997. Discovery of Early Triassic fish fossils and its significances in Jourong, Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu Geol, 21: 65-71 |
| [42] | Qiu X C, Xua Y L, Chen Z Q et al., The Early Triassic Jurong fish fauna, South China: age, anatomy, taphonomy, and global correlation. Glob Planet Change, 180: 33-50 |
| [43] | Regan C T, 1923. The skeleton of Lepidosteus , with remarks on the origin and evolution of the lower neopterygian fishes. Proc Zool Soc Lond, 1923: 445-461 |
| [44] | Romano C, Koot M B, Kogan I et al., 2016. Permian-Triassic Osteichthyes (bony fishes): diversity dynamics and body size evolution. Biol Rev, 91: 106-147 |
| [45] | Romano C, Jenks J F, Jattiot R et al., 2017. Marine Early Triassic Actinopterygii from Elko County (Nevada, USA): implications for the Smithian equatorial vertebrate eclipse. J Paleontol, 91: 1025-1046 |
| [46] | Schaeffer B, 1956. Evolution in the Subholostean Fishes. Evolution, 10: 201-212 |
| [47] | Schultze H P, 1966. Morphologische und histologische Untersuchungen an Schuppen mesozoischer Actinopterygier (Übergang von Ganoidzu Rundschuppen). Neues Jahrb Geol Paläont Abh, 126: 232-314 |
| [48] | Shen C C, Arratia G, 2022. Re-description of the sexually dimorphic peltopleuriform fish Wushaichthys exquisitus (Middle Triassic, China): taxonomic implications and phylogenetic relationships. J Syst Palaeont, 19: 1317-1342 |
| [49] | Stensiö E A, 1921. Triassic fishes from Spitzbergen. II. Kungl Svenska Vetenska Handl, 3: 1-261 |
| [50] | Stensiö E A, 1932. Triassic fishes from East Greenland. Medd Grønland, 83: 1-305 |
| [51] | Su D Z, 1981. A new species of Perleidus from Anhui. Vert PalAsiat, 19: 107-112 |
| [52] | Su D Z, 1993. New Jurassic ganoid fishes from northwestern Gansu, China. Vert PalAsiat, 31: 1-14 |
| [53] | Su D Z, Li Z C, 1983. A new Triassic perleidid fish from Hubei, China. Vert PalAsiat, 21: 9-17 |
| [54] | Sun Z Y, Tintori A, Lombardo C et al., 2008. A new species of the genus Colobodus Agassiz, 1844 (Osteichthyes, Actinopterygii) from the Pelsonian (Anisian, Middle Triassic) of Guizhou, South China. Riv Ital Paleont Stratigr, 114: 363-376 |
| [55] | Sun Z Y, Tintori A, Jiang D Y et al., 2009. A new perleidiform (Actinopterygii, Osteichthyes) from the Middle Anisian (Middle Triassic) of Yunnan, South China. Acta Geol Sin, 83: 460-470 |
| [56] | Swofford D L, 2003. PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts |
| [57] | Sytchevskaya E K, 1999. Freshwater fish fauna from the Triassic of Northern Asia. In: ArratiaG, SchultzeH P eds. Mesozoic Fishes 2 - Systematics and Fossil Record. München: Verlag Dr. 445-468 |
| [58] | Tintori A, Sassi D, 1992. Thoracopterus Bronn (Osteichthyes: Actinopterygii): a gliding fish from the Upper Triassic of Europe. J Vert Paleont, 12: 265-283 |
| [59] | Tong J N, Zhou X G, Erwin D H et al., 2006. Fossil fishes from the Lower Triassic of Majiashan, Chaohu, Anhui Province, China. J Paleontol, 80: 146-161 |
| [60] |
Wen W, Hu S X, Zhang Q Y et al., 2019. A new species of Platysiagum from the Luoping Biota (Anisian, Middle Triassic, Yunnan, South China) reveals the relationship between Platysiagidae and Neopterygii. Geol Mag, 156: 669-682
DOI |
| [61] | Westoll T S, 1944. The Haplolepidae, a new family of Late Carboniferous bony fishes - a study in taxonomy and evolution. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist, 83: 1-121 |
| [62] | Xu G H, 2020a. Feroxichthys yunnanensis gen. et sp. nov. (Colobodontidae, Neopterygii), a large durophagous predator from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) Luoping Biota, eastern Yunnan, China. PeerJ, 8: e10229 |
| [63] | Xu G H, 2020b. A new species of Luganoia (Luganoiidae, Neopterygii) from the Middle Triassic Xingyi Biota, Guizhou, China. Vert PalAsiat, 59: 169-199 |
| [64] | Xu G H, 2021a. A new stem-neopterygian fish from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Yunnan, China, with a reassessment of the relationships of early neopterygian clades. Zool J Linn Soc, 191: 375-394 |
| [65] | Xu G H, 2021b. The oldest species of Peltoperleidus (Louwoichthyiformes, Neopterygii) from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of China, with phylogenetic and biogeographic implications. PeerJ, 9: e12225 |
| [66] | Xu G H, Ma X Y, 2016. A Middle Triassic stem-neopterygian fish from China sheds new light on the peltopleuriform phylogeny and internal fertilization. Sci Bull, 61: 1766-1774 |
| [67] | Xu G H, Zhao L J, 2016. A Middle Triassic stem-neopterygian fish from China shows remarkable secondary sexual characteristics. Sci Bull, 61: 338-344 |
| [68] | Xu G H, Zhao L J, Gao K Q et al., 2012. A new stem-neopterygian fish from the Middle Triassic of China shows the earliest over-water gliding strategy of the vertebrates. Proc R Soc B, 280: 20122261 |
| [69] | Xu G H, Gao K Q, Coates M I, 2015. Taxonomic revision of Plesiofuro mingshuica from the Lower Triassic of northern Gansu, China, and the relationships of early neopterygian clades. J Vert Paleont, 35: e1001515 |
| [70] | Yuan Z W, Xu G H, Dai X et al., 2022. A new perleidid neopterygian fish from the Early Triassic (Dienerian, Induan) of South China, with a reassessment of the relationships of Perleidiformes. PeerJ, 10: e13448 |
| [71] | Zhao L J, Lu L W, 2007. A new genus of Early Triassic perleidid fish from Changxing, Zhejiang, China. Acta Palaeontol Sin, 46: 238-243 |
| [1] | CHEN Yang, LI Qiang, ZHOU Zheng-Da, SHAN Xian-Ren, ZHU You-An, WANG Qian, WEI Guang-Biao, ZHU Min. A new genus of galeaspids (jawless stem-Gnathostomata) from the early Silurian Chongqing Lagerstätte, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2024, 62(4): 245-261. |
| [2] | SHI Yu-Tai, LIU Jun. Osteology of Turfanodon bogdaensis (Dicynodontia) . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2024, 62(3): 186-200. |
| [3] | LIU Jun, Fernando ABDALA. A new small baurioid therocephalian from the Lower Triassic Jiucaiyuan Formation, Xinjiang, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2024, 62(3): 201-224. |
| [4] | LUO Yan-Chao, ZHU Min, LU Li-Wu, PAN Zhao-Hui. Reappraisal of Bothriolepis sinensis Chi, 1940 from the Tiaomachien Formation, Hunan, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2023, 61(4): 261-276. |
| [5] | FENG Dong-Hao, XU Guang-Hui, MA Xin-Ying, REN Yi. Taxonomic revision of Sinoeugnathus kueichowensis (Halecomorphi, Holostei) from the Middle Triassic of Guizhou and Yunnan, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2023, 61(3): 161-181. |
| [6] | REN Yi, XU Guang-Hui. A new species of Pteronisculus from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Luoping, Yunnan, China, and phylogenetic relationships of early actinopterygian fishes . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2021, 59(3): 169-199. |
| [7] | XU Guang-Hui. A new species of Luganoia (Luganoiidae, Neopterygii) from the Middle Triassic Xingyi Biota, Guizhou, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2020, 58(4): 267-282. |
| [8] | XU Guang-Hui, MA Xin-Ying, WU Fei-Xiang, REN Yi. A Middle Triassic kyphosichthyiform from Yunnan, China, and phylogenetic reassessment of early ginglymodians . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2019, 57(3): 181-204. |
| [9] | LIAO Chun-Chi, XU Xing. Cranial osteology of Beipiaosaurus inexpectus(Theropoda: Therizinosauria) . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2019, 57(2): 117-132. |
| [10] | WANG Min, Jingmai O’CONNOR, ZHOU Zhong-He. A taxonomical revision of the Confuciusornithiformes (Aves: Pygostylia) . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2019, 57(1): 1-37. |
| [11] | RONG Yu-Fen. Restudy of Regalerpeton weichangensis (Amphibia: Urodela) from the Lower Cretaceous of Hebei, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2018, 56(2): 121-136. |
| [12] | Luoping, Yunnan; Triassic; Ionoscopiformes, Halecomorphi;osteology; phylogeny . A new ionoscopiform fish (Holostei: Halecomorphi) from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Yunnan, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2017, 55(2): 162-176. |
| [13] | QIU Zhu-Ding JIN Chang-Zhu . Sciurid remains from the Late Cenozoic fissure-fillings of Fanchang, Anhui, China . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2016, 54(4): 286-301. |
| [14] | K. Christopher BEARD, NI Xi-Jun, WANG Yuan-Qing , MENG Jin , Daniel L. GEBO. Dentition of Subengius mengi (Mammalia: Plesiadapoidea) and a reassessment of the phylogenetic relationships of Asian Carpolestidae . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2016, 54(3): 181-211. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhao-Qun, LI Chuan-Kui, WANG Jian, WANG Yuan-Qing, MENG Jin . Presence of the calcaneal canal in basal Glires . Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2016, 54(3): 235-242. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||